Hangman’s fracture
Hangman’s fracture
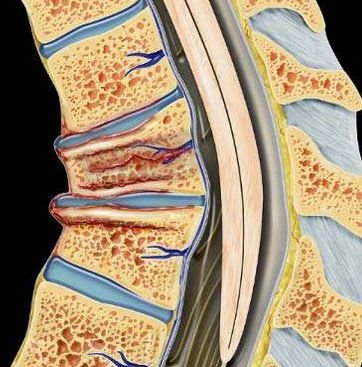
Hangman’s fracture is a specific type of cervical spine injury involving a bilateral fracture through the pars interarticularis of the second cervical vertebra (C2), also known as the axis. This type of injury gets its name from the position and force associated with judicial hangings, though in modern times, it is far more commonly caused by high-speed trauma, especially road traffic accidents and falls. In the context of Bangladesh, Hangman’s fracture is increasingly observed due to rising motorbike crashes, rickshaw or auto-rickshaw collisions, falls from unguarded rooftops, and sports or diving injuries. These injuries are extremely dangerous as the C2 vertebra is closely associated with the spinal cord, and any displacement can lead to quadriplegia or sudden death. Importance of Early Diagnosis and Surgical Expertise in Bangladesh In most regions of Bangladesh, access to immediate cervical spine imaging and specialized neurosurgical care is limited. As a result, many Hangman’s fractures remain misdiagnosed or improperly treated, which increases the risk of delayed paralysis or life-threatening complications. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, a leading expert in pediatric and adult cervical spine trauma, provides advanced evaluation and surgical care for Hangman’s fractures at the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre. Common Causes of Hangman’s Fracture in Bangladesh Motorbike or car accidents (high-speed trauma) Falls from rooftops, trees, or stairs Diving into shallow water Pedestrian injuries in busy traffic zones Non-accidental trauma or child abuse (in rare pediatric cases) Industrial or construction site falls without helmets Symptoms of Hangman’s Fracture The severity of symptoms varies depending on the fracture type and spinal stability: Neck pain and stiffness Loss of neck mobility Muscle weakness or paralysis in arms and legs Difficulty breathing or swallowing (in severe cases) Loss of consciousness in high-energy trauma Tingling or numbness in limbs In children: crying with neck movement, refusal to move neck or head Classification of Hangman’s Fracture Hangman’s fracture is commonly classified by the Levine and Edwards system into: Type I: Non-displaced with stable alignment Type II: Displaced with angulation or ligament injury Type IIA: Minimal displacement but significant angulation due to ligament damage Type III: Severe displacement with C2-C3 facet dislocation The type of fracture determines whether surgical or conservative management is appropriate. Diagnostic Approach in Bangladesh Advanced imaging is essential for diagnosing and planning treatment: CT scan of cervical spine: Essential for bone assessment and classifying fracture type MRI cervical spine: Evaluates ligament injury and spinal cord involvement Dynamic X-rays: Used cautiously to assess instability only after stabilization Dr. Nafaur Rahman’s team uses 3D reconstructions and pre-op planning software to ensure the highest standards in diagnosis and surgical outcomes. Treatment Strategies The goal of treatment is to ensure spinal alignment, stabilization, and prevention of neurological deterioration. ✅ Non-Surgical Management (Type I, selected Type II) Rigid cervical collar or halo vest immobilization for 6–12 weeks Pain control and anti-inflammatory medications Serial imaging to monitor healing Physiotherapy and gradual neck mobilization post-immobilization This approach is suitable when the fracture is stable and there’s no neurological deficit. ✅ Surgical Management (Type II, IIA, and Type III) Surgery is often required when the fracture is unstable, significantly displaced, or if there’s spinal cord involvement. Surgical techniques include: C2 pedicle or pars screw fixation Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) at C2-C3 Posterior cervical fusion using rods and screws Occipitocervical fusion in complex craniovertebral injuries Intraoperative neuro-monitoring to prevent spinal cord damage Dr. Nafaur Rahman performs these procedures using minimally invasive techniques, where applicable, to reduce blood loss and improve recovery. Postoperative Recovery ICU observation for high-risk cases Neck bracing for several weeks post-surgery Physiotherapy and gait training Speech or respiratory support if cranial nerves are affected Follow-up imaging to ensure fusion success Prognosis in Bangladesh With timely and appropriate treatment, most Hangman’s fractures have a favorable outcome, especially if the spinal cord has not been injured. Delayed diagnosis, however, can result in permanent disability or sudden death. Why Trust Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman for Cervical Spine Trauma? ✔️ Specialized in C2 fractures and high cervical injuries ✔️ Trained in advanced spinal instrumentation techniques ✔️ Extensive experience managing complex craniovertebral junction injuries ✔️ Works at Bangladesh’s top neurosurgical center (NINS) ✔️ Personalized care for both pediatric and adult patients ✔️ Offers world-class spinal surgery within the Bangladesh healthcare framework Book an Urgent Consultation for Hangman’s Fracture 📌 Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment 📞 +8801912988182 | +8801607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com