Spinal Infections
Spinal Infections
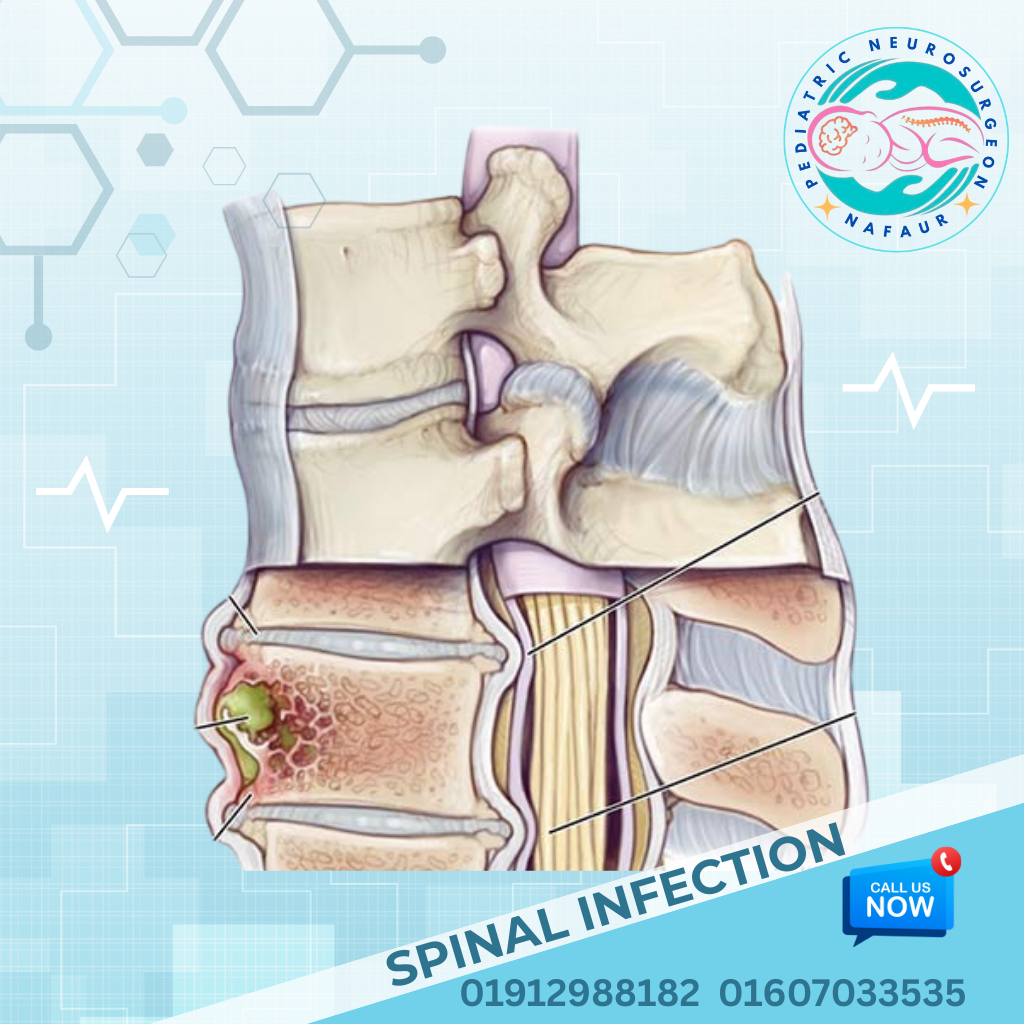
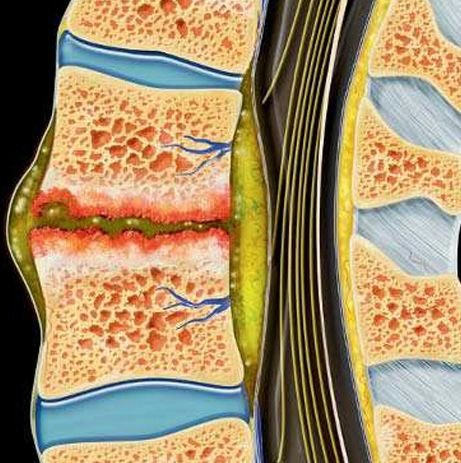
Pediatric spinal infections are serious conditions in which bacteria, viruses, fungi, or tuberculosis organisms infect parts of the spine such as the vertebrae, intervertebral discs, spinal cord, or epidural space. These infections, if not identified and treated early, can result in neurological deficits, spinal deformities, paralysis, or even death in severe cases. Children in Bangladesh are especially vulnerable to spinal infections due to various socio-economic and environmental factors. Delayed diagnosis, lack of advanced imaging in rural areas, and the presence of drug-resistant tuberculosis increase the burden of pediatric spinal infections in the country. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, one of Bangladesh’s leading pediatric neurosurgeons, provides specialized diagnosis and surgical management of these complex conditions at the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre. 🌍 Pediatric Spinal Infections in Bangladesh: A Growing Concern In the Bangladeshi context, spinal infections in children often present late and misdiagnosed, with many cases first treated as general back pain or fever. The absence of awareness, poor access to imaging (MRI/CT), and delayed referrals to pediatric neurosurgeons contribute to permanent disability in many affected children. Common Contributing Factors in Bangladesh: 🏚️ Overcrowded living conditions and poor sanitation 🧬 Malnutrition and immune suppression 🩸 Exposure to infected adults with tuberculosis ⏱️ Late recognition of neurological signs in rural healthcare settings ❌ Incomplete or irregular antibiotic treatment “Infections of the spine in children are treatable—if we diagnose them early and intervene with precision.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman ⚠️ Signs and Symptoms of Pediatric Spinal Infections Symptoms may vary depending on the type and location of infection. Common symptoms include: 🧍 Severe back or neck pain (often localized) 🌡️ Persistent fever and malaise 🧒 Reluctance to walk or move 🧑🦽 Progressive limb weakness or paralysis 🛌 Loss of bladder/bowel control 🦴 Spinal deformities like gibbus (hump) in spinal TB 🤕 Localized tenderness over the spine Parents and physicians should be alert when a child presents with fever plus back pain and difficulty walking. 🧬 Types and Causes of Spinal Infections in Children Pediatric spinal infections can involve different parts of the spinal column or surrounding structures. 🔬 Common Types: Spondylodiscitis – Infection of vertebrae and disc space Epidural Abscess – Collection of pus compressing the spinal cord Vertebral Osteomyelitis – Infection of the spinal bone Pott’s Disease (Spinal TB) – Common in Bangladesh, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis Spinal Meningitis with abscess Postoperative spinal infections 🦠 Causative Organisms: Staphylococcus aureus – most common in acute bacterial cases Mycobacterium tuberculosis – most common in chronic infections Fungal pathogens – in immunocompromised children Gram-negative bacteria – in neonatal intensive care settings 🧪 Diagnostic Approach Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman utilizes a detailed clinical assessment, supported by advanced imaging and laboratory tests to reach a definitive diagnosis. Essential Diagnostics: 🧲 MRI Spine with Contrast – Gold standard for infection and cord compression 📸 X-ray Spine – May show vertebral destruction or deformity in TB 🧬 CT Scan Spine – For bone detail and surgical planning 🧪 Blood tests – CBC, ESR, CRP (typically raised) 💉 Blood culture or TB-PCR from spinal lesion aspirate 🧫 Biopsy – In cases of diagnostic uncertainty or for drug sensitivity testing “A missed or delayed diagnosis of spinal TB in a child can result in irreversible paralysis.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🛠️ Treatment of Pediatric Spinal Infections Treatment strategies depend on the type, location, and severity of infection and neurological involvement. 💊 Medical Treatment: IV antibiotics for 4–6 weeks in bacterial infections Anti-tubercular therapy (ATT) for 12–18 months in spinal TB Steroids to reduce inflammation (especially in TB meningitis) Antifungal therapy in select cases Nutritional rehabilitation 🧠 Surgical Management: Surgical intervention is needed if: There is spinal cord compression Neurological deficits worsen Presence of epidural abscess Failed response to medical therapy Spinal instability or deformity Common Surgical Procedures: Laminectomy or Laminotomy – For decompression and pus evacuation Debridement and drainage – Of infected tissue Spinal fixation – In cases of instability or deformity Image-guided biopsy – To confirm diagnosis and guide treatment Dr. Nafaur Rahman uses minimally invasive techniques whenever possible to reduce surgical risks and recovery time in children. 🔁 Post-Treatment Care and Rehabilitation Recovery from spinal infections requires a holistic and prolonged follow-up strategy: 🧠 Neurological exams and motor recovery tracking 🏥 Repeat MRI scans to confirm infection resolution 🧑🦽 Physiotherapy and gait training for paralyzed children 🧒 Nutritional and immunity-boosting programs 🧑🏫 Support for returning to school and normal life 🚨 Complications of Untreated or Delayed Pediatric Spinal Infection 🧠 Permanent spinal cord damage 🛌 Paralysis or bladder dysfunction 🧑🦽 Spinal deformity requiring corrective surgery 💀 Sepsis or death in severe untreated cases 📉 Poor growth and delayed development Early referral to a pediatric neurosurgeon is critical in avoiding such complications. 👨⚕️ Why Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🎓 Renowned Pediatric Neurosurgeon in Bangladesh 🏥 Expert in spinal infection surgery and neurorehabilitation 🔍 Specialist in pediatric spinal TB and postoperative infections 🌐 Treats patients from both urban and rural backgrounds 🤝 Offers multidisciplinary care including nutrition, physio, and pediatric support 📞 Contact Dr. Nafaur Rahman for Evaluation and Treatment Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com
Types of Spinal Infections