Myelomeningocele
Myelomenigocele
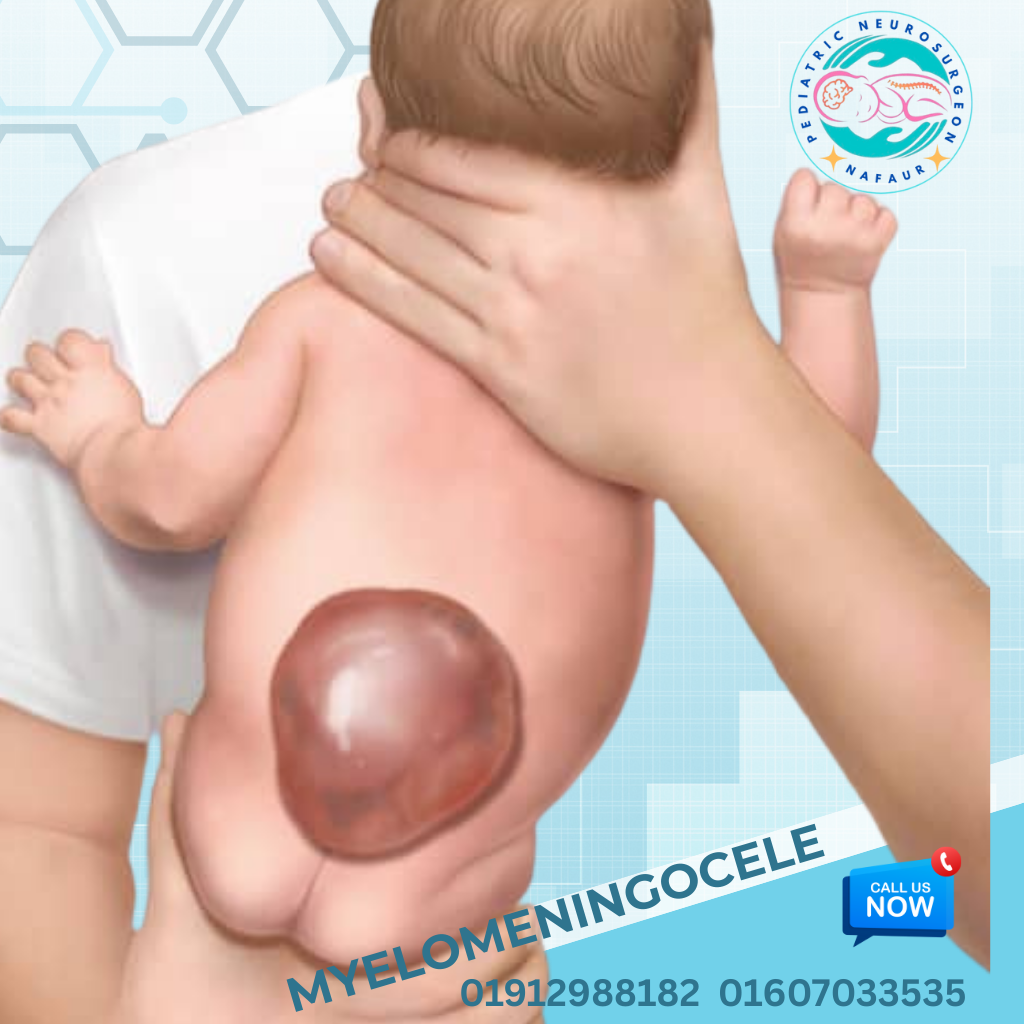
Myelomeningocele is the most severe form of spina bifida, a type of neural tube defect (NTD) where the spinal cord and meninges protrude through an opening in the baby’s back, typically along the lower spine. It develops during the first month of pregnancy, often before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
In Bangladesh, a significant number of infants are born each year with untreated or late-diagnosed myelomeningocele, largely due to a lack of prenatal screening, nutritional awareness, and access to specialized surgical care. With timely neurosurgical intervention and long-term support, many of these children can lead productive lives.
🔬 Causes and Risk Factors
Myelomeningocele occurs due to incomplete closure of the neural tube during early fetal development. Contributing risk factors include:
Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy
Maternal diabetes or obesity
Exposure to certain medications or toxins
Family history of neural tube defects
Low awareness and poor antenatal care in rural areas of Bangladesh
Despite its preventability, many families are unaware of folic acid supplementation, leading to a higher incidence of myelomeningocele in underserved communities.
🧒 Symptoms of Myelomeningocele
The severity of symptoms depends on the location and extent of the spinal defect, but common signs include:
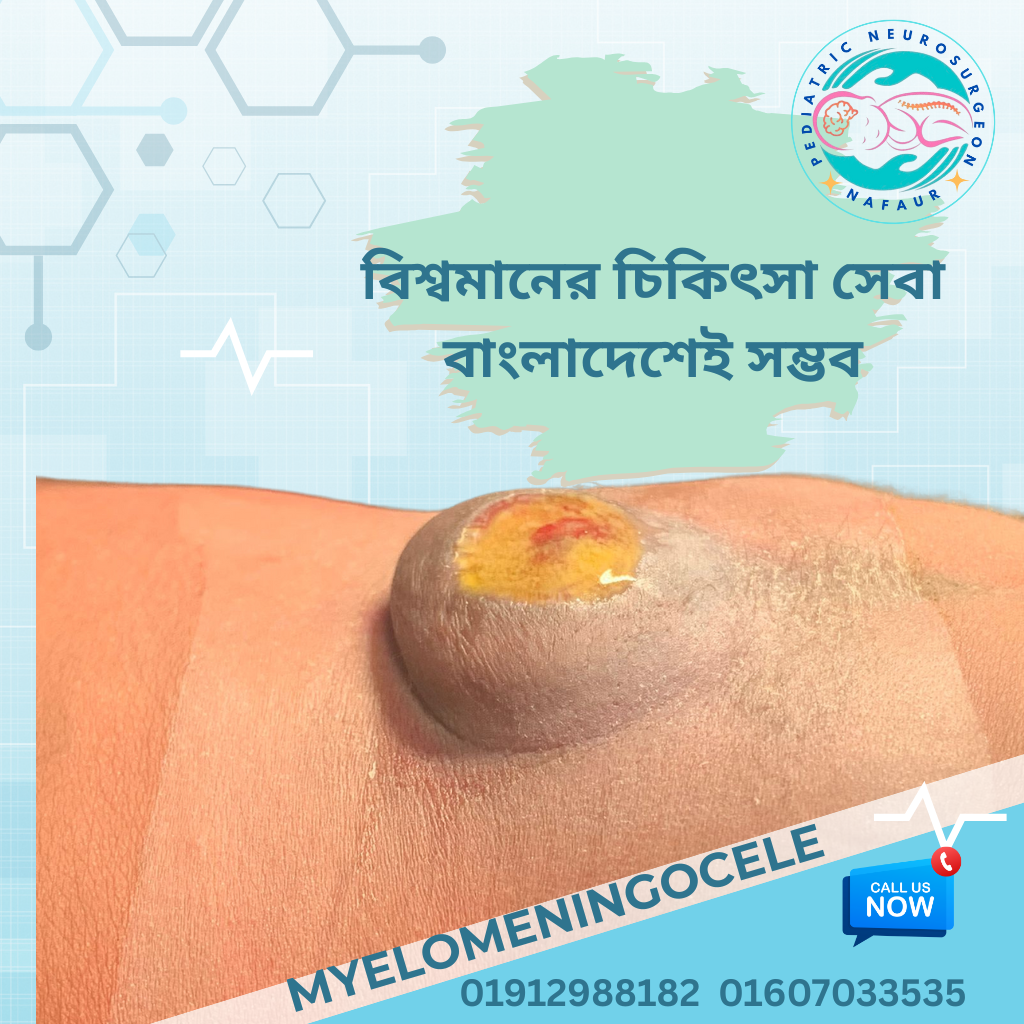
1.Visible sac on the back containing spinal cord tissue
2.Partial or complete paralysis of the lower limbs
3.Loss of bladder and bowel control
4.Hydrocephalus (fluid accumulation in the brain)
5.Orthopedic deformities like clubfoot or scoliosis
6.Cognitive or developmental delays (in severe cases)
In Bangladesh, many children with this condition present late to hospitals due to financial barriers and lack of transportation to specialized centers like NINS.
🧪 Diagnosis
Prenatal Diagnosis:
Ultrasound at 18–22 weeks can detect open neural tube defects
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) testing
Fetal MRI for detailed assessment (less available in Bangladesh)
Postnatal Diagnosis:
Physical examination of the spinal lesion
MRI or CT scan to assess the spinal cord
Ultrasound of the brain to detect hydrocephalus
Urodynamic studies to assess bladder function
Dr. Nafaur emphasizes early imaging and multidisciplinary evaluation for every diagnosed case.
🛠️ Surgical Treatment of Myelomeningocele
Surgery is the first critical step in managing myelomeningocele. The goal is to:
Close the open spinal cord and skin defect
Prevent infection, especially meningitis
Preserve whatever neurological function remains
Reduce future complications
🏥 Common Surgical Procedures:
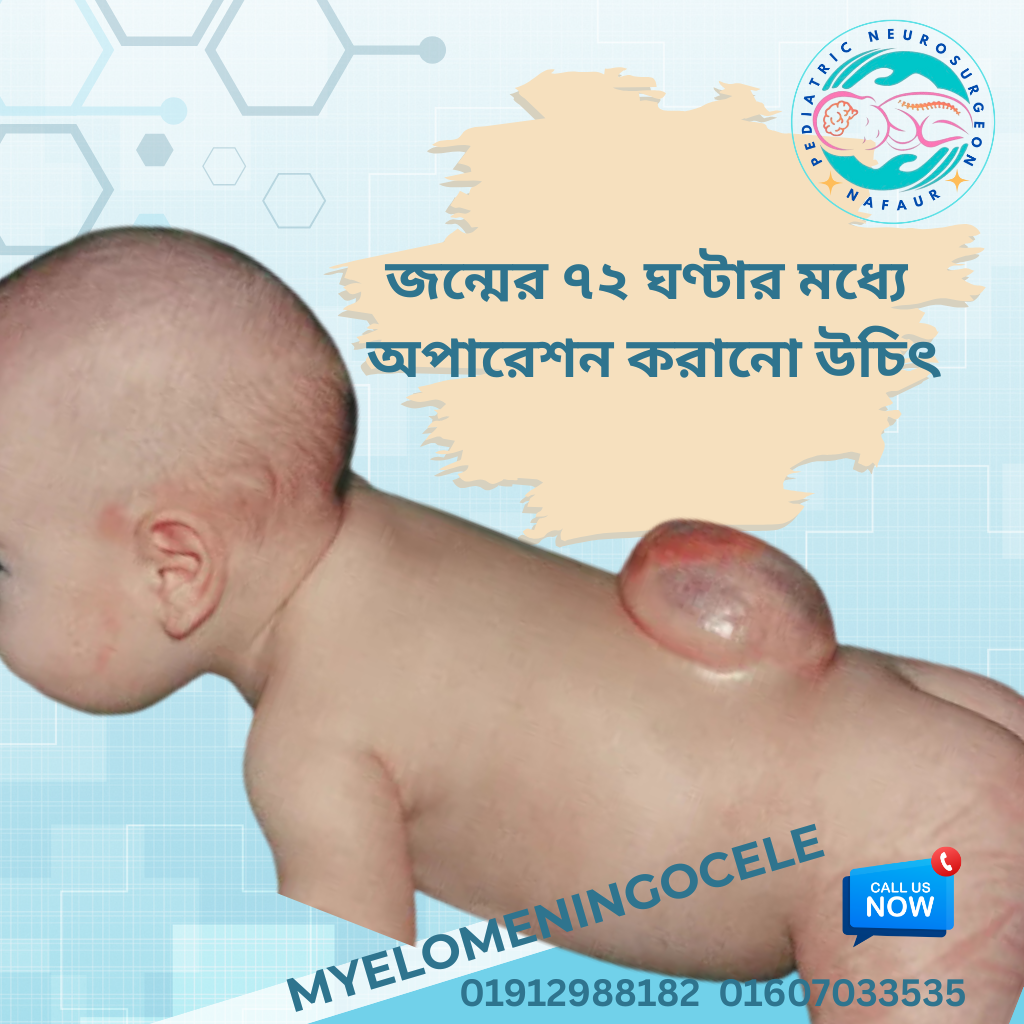
✅ Early Surgical Closure (within 48–72 hours)
Prevents infection and preserves neural tissue
Dr. Nafaur performs this delicate microsurgery at NINS with expert care
✅ VP Shunt Placement
For children with hydrocephalus, ventriculoperitoneal shunt is placed to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid
✅ Orthopedic and Urological Surgeries
Managed in collaboration with physiatrists and pediatric urologists
"Timely closure of the myelomeningocele and appropriate follow-up can dramatically improve a child’s lifespan and quality of life." — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman
🧠 Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Post-surgical management includes:
Antibiotics and wound care
Monitoring for shunt infection or malfunction
Bladder and bowel training
Physical therapy to improve mobility
Orthotic support and management of foot deformities
Parental counseling and home care training
At the Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre, Dr. Nafaur and his team provide multidisciplinary care designed to empower families.
🌟 Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
While myelomeningocele is a lifelong condition, early intervention and comprehensive care can significantly improve outcomes:
Many children walk with braces or walkers
Some may have normal intelligence, others may need special education
Proper bladder management helps prevent kidney damage
Vocational training helps many become independent adults
In Bangladesh, long-term success depends on access to care, public health awareness, and family support systems.

Types of Myelomeningocele