Anencephaly
Anencephaly
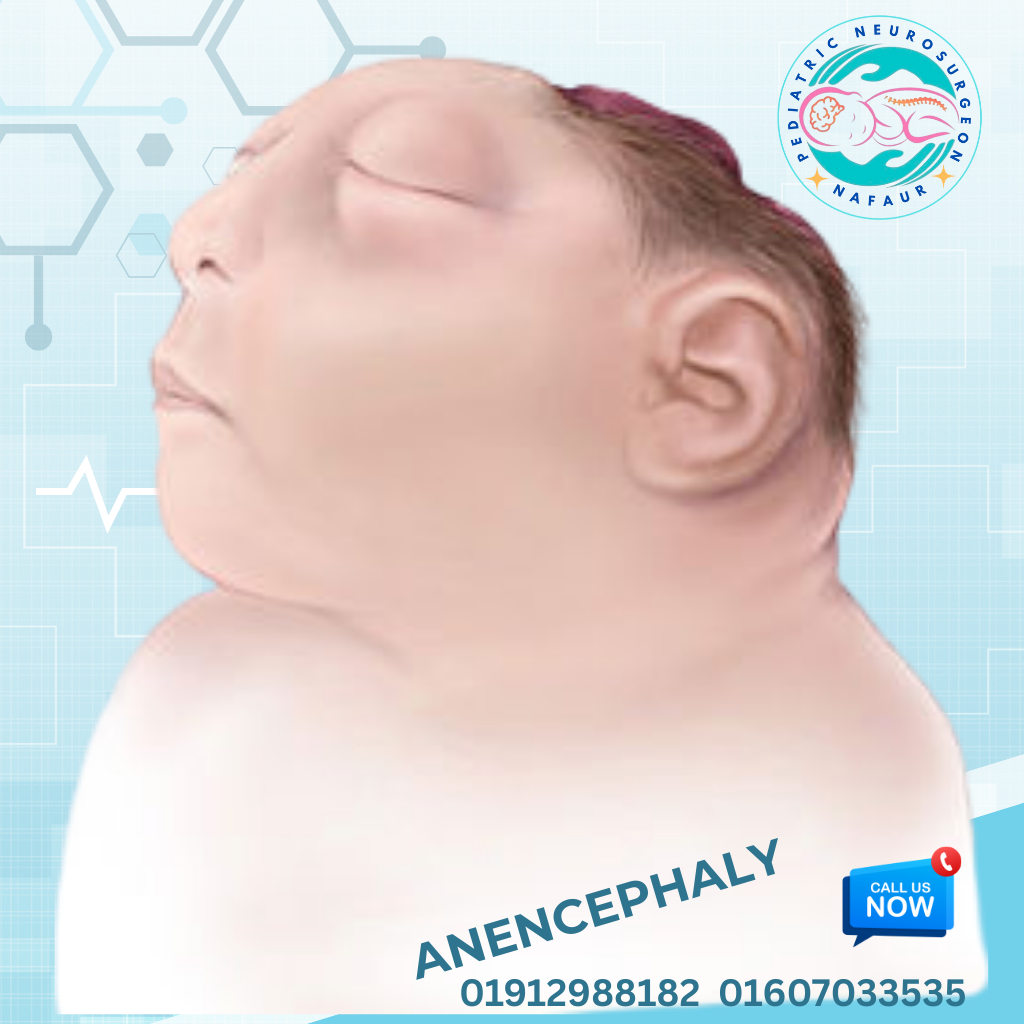
Anencephaly is a severe, fatal neural tube defect (NTD) in which a large portion of a baby’s brain, skull, and scalp fails to develop during early embryonic growth. It occurs when the upper part of the neural tube, which forms the brain and skull, does not close properly during the third to fourth week of pregnancy. As a result, the newborn is born without a significant part of the brain, particularly the forebrain and cerebral hemispheres, which are necessary for thinking, vision, hearing, and consciousness. Anencephaly is classified as a congenital and non-compatible-with-life disorder, meaning that affected infants are either stillborn or die within hours or days after birth. 🌍 Anencephaly in the Bangladesh Perspective In Bangladesh, awareness about neural tube defects like anencephaly is relatively low, particularly in rural communities Many pregnancies are unplanned and unmonitored, leading to missed opportunities for early diagnosis and preventive care Lack of routine prenatal folic acid supplementation contributes to higher incidence rates In many regions, anencephaly is misunderstood, sometimes linked with superstitions, causing emotional distress among parents Access to fetal anomaly scanning and genetic counseling is limited outside major cities like Dhaka Management requires sensitive counseling, accurate diagnosis, and public health education ⚠️ Causes and Risk Factors Anencephaly is caused by failure of the neural tube to close at the cranial end during early fetal development. Contributing factors include: Folic acid deficiency before and during early pregnancy Genetic predisposition and chromosomal abnormalities Maternal diabetes, obesity, and certain medications (e.g., anti-epileptic drugs) Exposure to toxins or infections during early pregnancy Previous history of neural tube defects in siblings 🧒 Signs and Symptoms Absence of the major portions of the brain and skull, visible at birth Newborn typically appears unconscious, blind, deaf, and unable to feel pain Lack of scalp and cranial bones over a large portion of the head Facial abnormalities or open skull deformity Reflexive movements (e.g., breathing, crying) may be present but no higher brain function exists In most cases, affected babies are stillborn or survive only a few hours/days 🔍 Diagnosis and Prenatal Detection Early diagnosis is crucial and can be made through: Maternal Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP) Test Elevated AFP levels in the second trimester may indicate an open neural tube defect Ultrasound Scanning High-resolution fetal anomaly scan between 16–20 weeks of pregnancy can detect absent cranial bones and brain tissues Often reveals a “frog-eye appearance” due to exposed orbits and absent cranial vault Amniocentesis May be done to assess genetic conditions or confirm diagnosis 🚫 Prognosis and Treatment Unfortunately, there is no cure or surgical treatment for anencephaly. The condition is uniformly fatal due to: Absence of functional brain tissue Inability to breathe, eat, or survive independently Management Strategies: Supportive care and palliative management after birth Counseling of parents for emotional and psychological support Prenatal counseling regarding the prognosis and options, including continuation or termination of pregnancy where legal Autopsy and genetic testing (when consented) to guide future pregnancies 🌱 Prevention and Public Health Awareness Folic Acid Supplementation: Taking 400–800 mcg of folic acid daily before conception and during the first trimester can reduce the risk of anencephaly by up to 70% Health education campaigns in Bangladesh should prioritize folic acid awareness, especially in low-resource areas Routine antenatal check-ups with trained professionals and anomaly scans during pregnancy Community education to remove stigma and prevent misinformation about congenital brain defects 👨⚕️ Why Consult Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Renowned pediatric neurosurgeon with a focus on congenital brain and spinal disorders Extensive experience at National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS), Dhaka Chief Consultant at Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre, leading prenatal counseling services for high-risk pregnancies Offers compassionate, evidence-based guidance to expecting parents facing fetal anomalies Advocates for public health awareness and early diagnosis in underserved populations across Bangladesh 📞 Contact for Expert Fetal Neurocounseling Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Appointment Hotline: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com