Others
Other Congenital and Developmental Brain Disorder
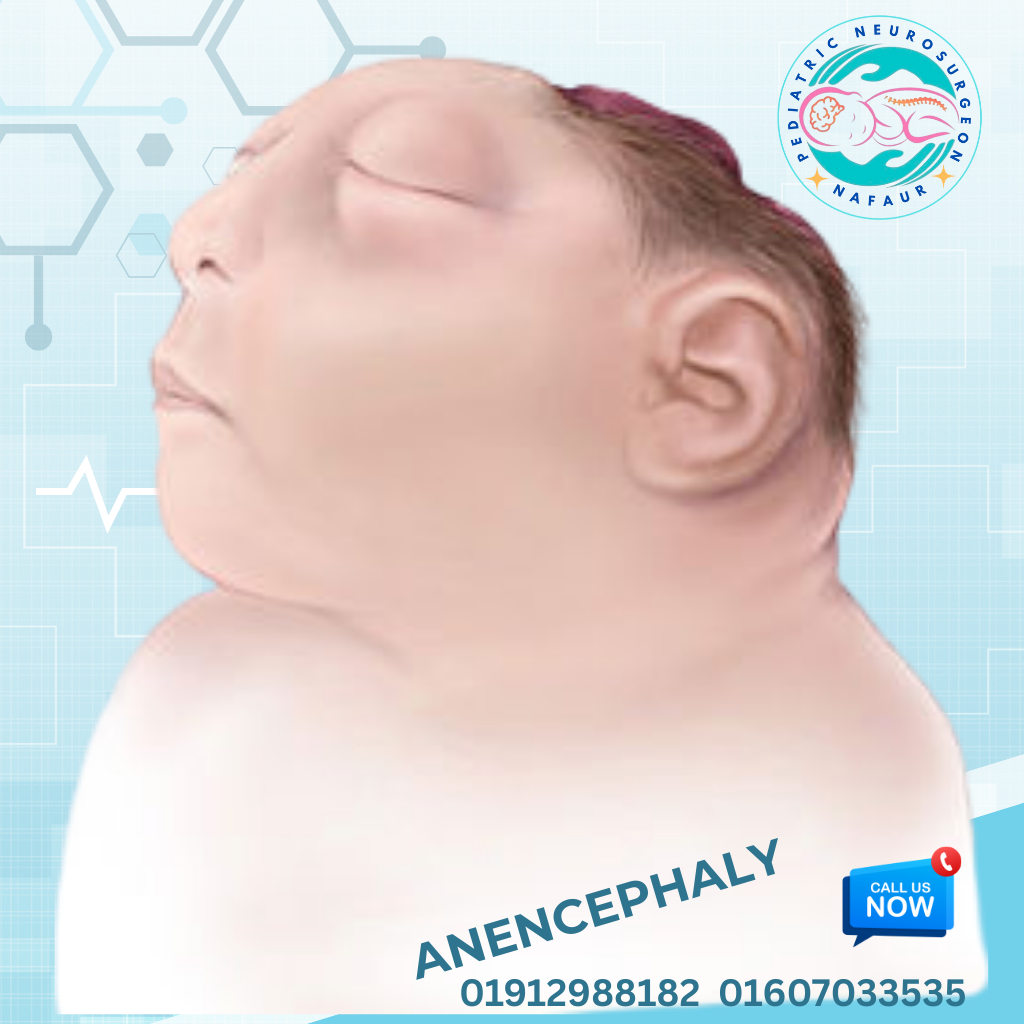
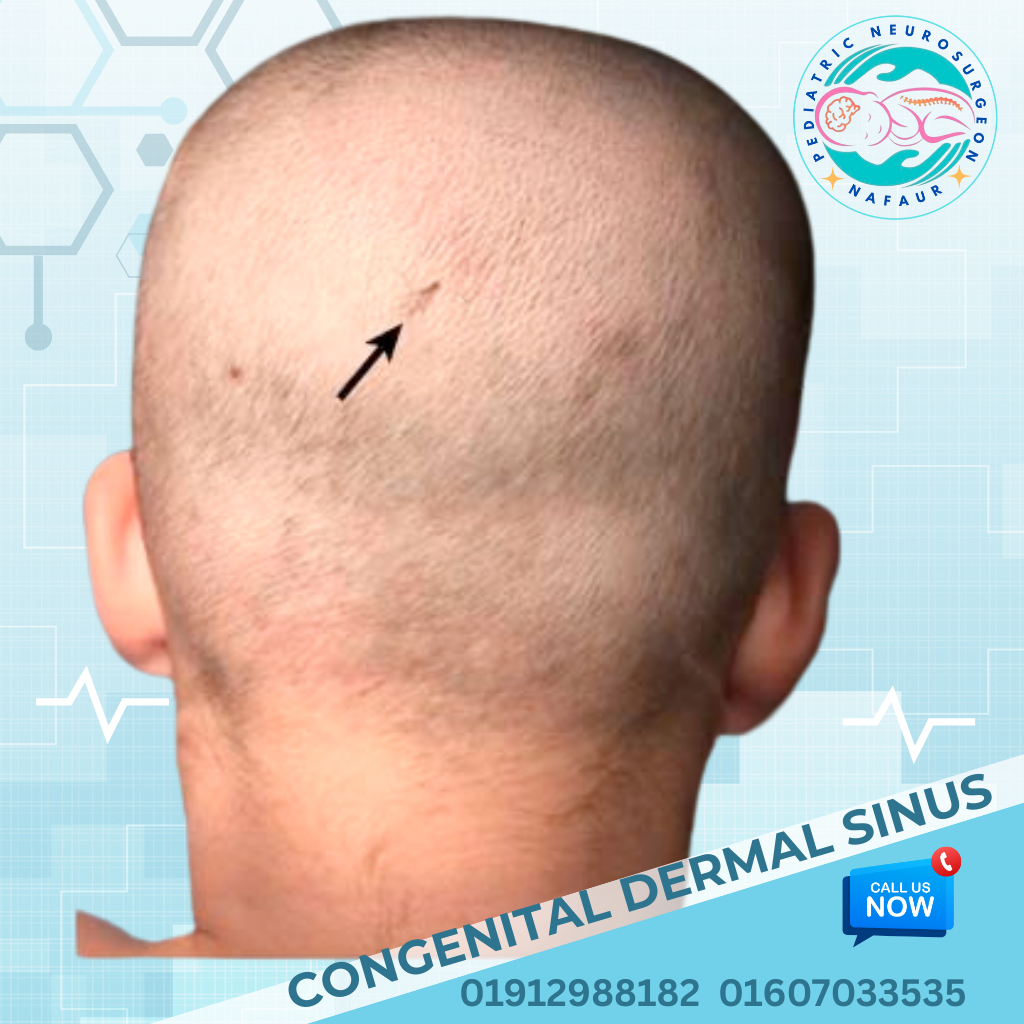
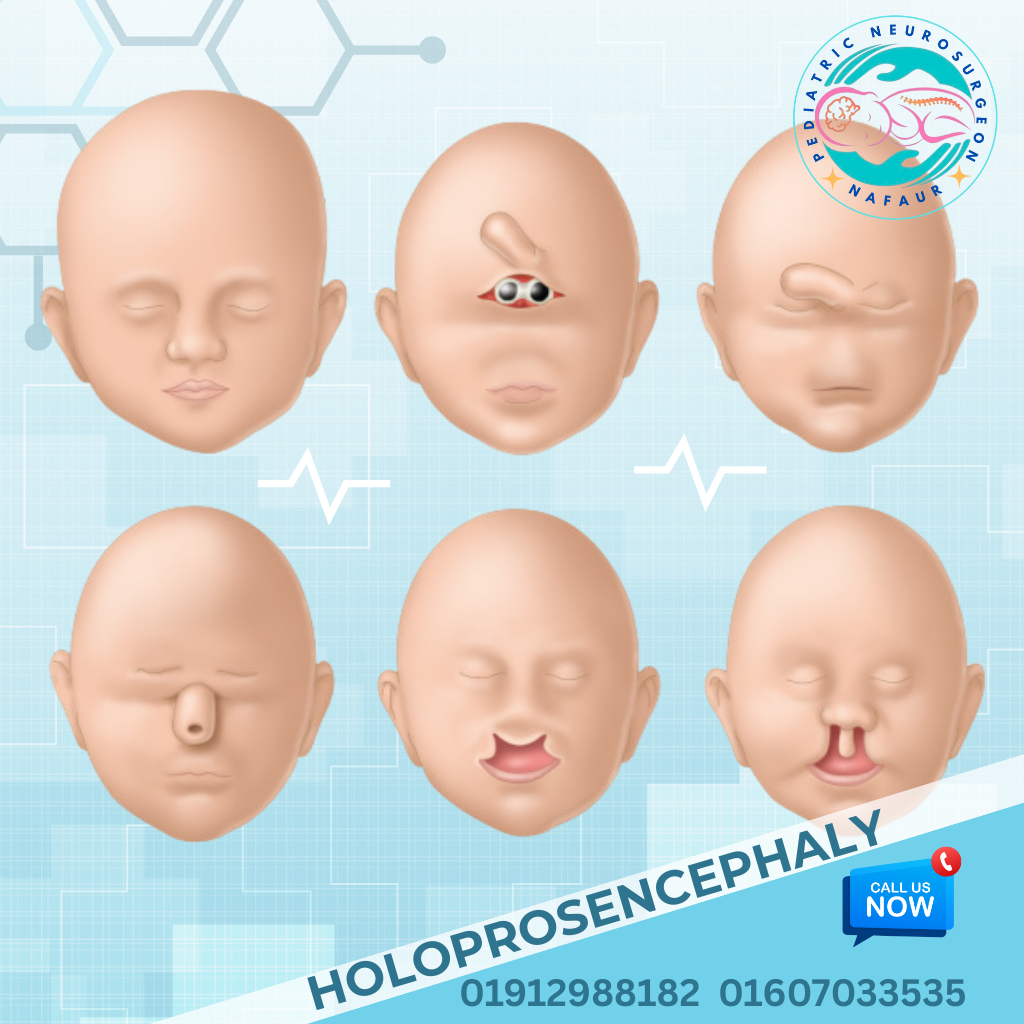
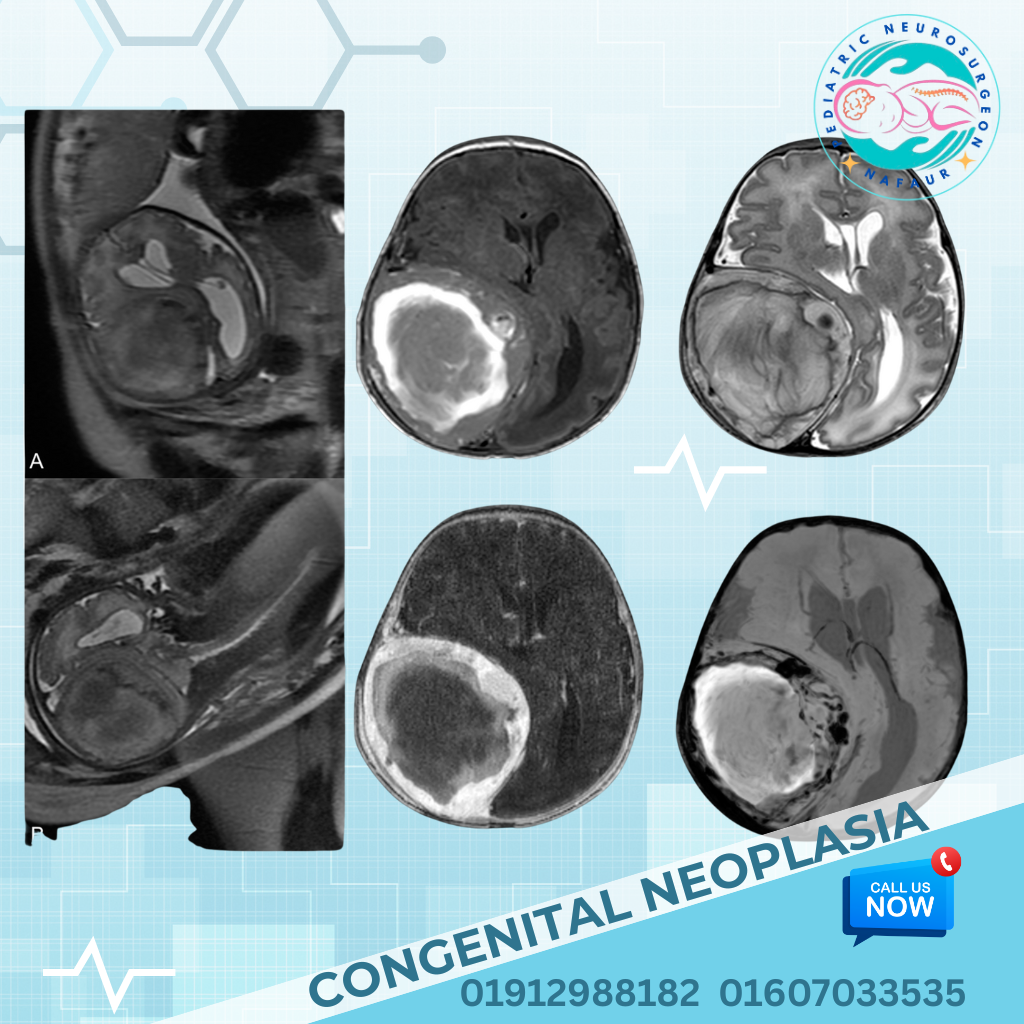
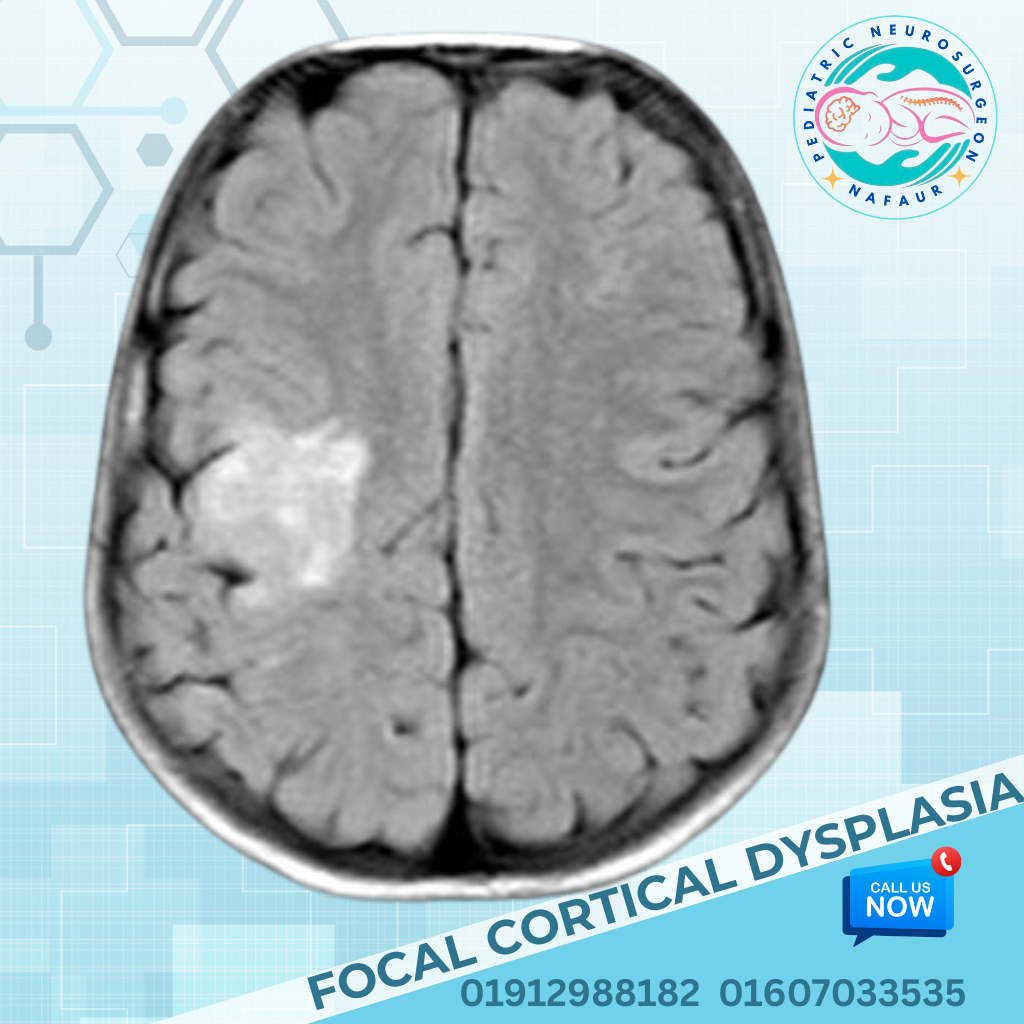
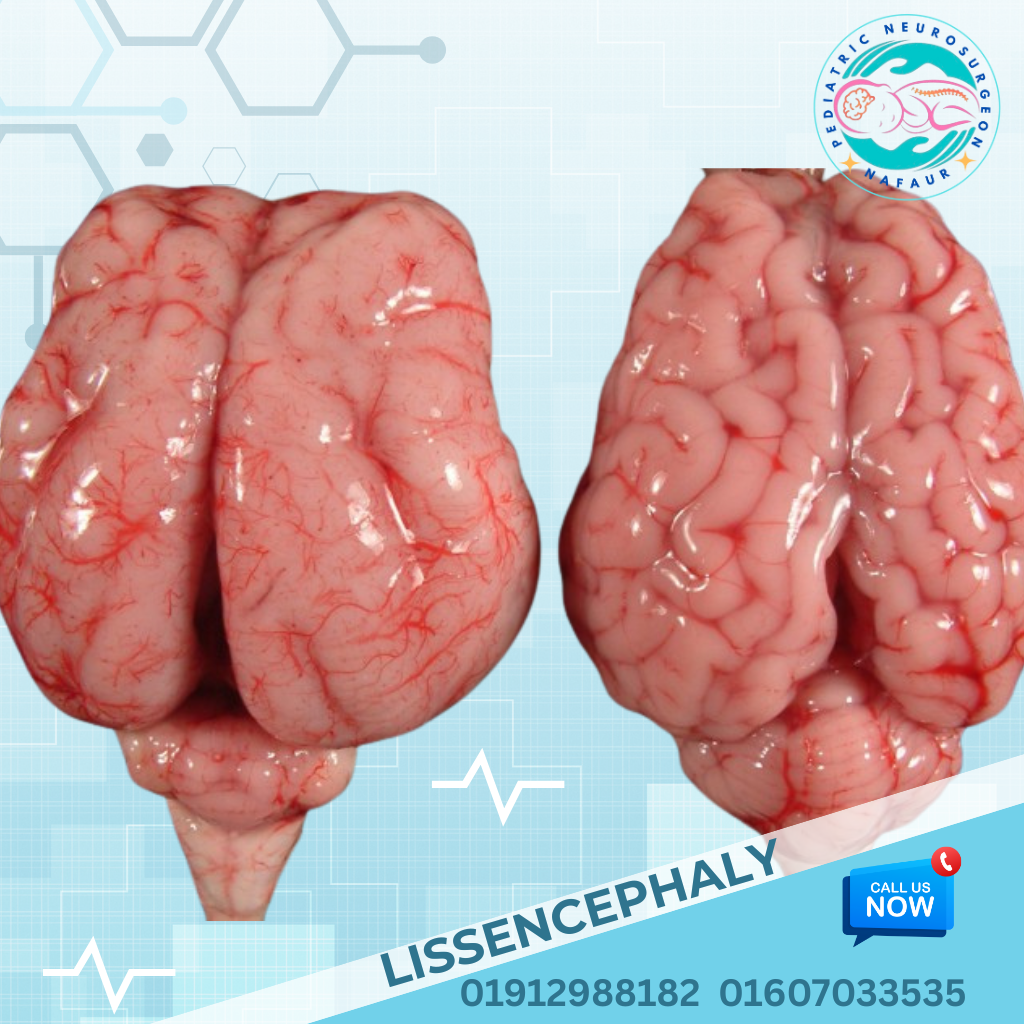
Rare congenital brain disorders are uncommon but serious neurological conditions present at birth, caused by abnormal development of the fetal brain. These may result in structural malformations, neurological deficits, seizures, developmental delays, or hydrocephalus. Some of these conditions are genetically inherited, while others are due to intrauterine infections, environmental factors, or unknown causes. In Bangladesh, early diagnosis is often missed due to lack of prenatal imaging, limited access to pediatric neuroimaging, and delayed referral to specialists. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, one of the country’s leading pediatric neurosurgeons, is committed to offering accurate diagnosis, advanced neurosurgical treatment, and multidisciplinary care for rare congenital brain disorders, helping children achieve the best possible outcomes. 🌍 Rare Brain Disorders – A Hidden Pediatric Challenge in Bangladesh Despite improvements in maternal and child health in Bangladesh, rare brain malformations continue to be: 🚫 Undiagnosed until symptoms worsen (e.g., seizures, head enlargement, developmental delay) ❌ Mislabeled as idiopathic intellectual disability or autism 🏥 Undertreated due to lack of specialized pediatric neurosurgical expertise ⚠️ Mismanaged at general facilities, delaying effective intervention 🧬 Examples of Rare Congenital Brain Disorders Holoprosencephaly Failure of the brain to divide into two hemispheres May cause facial deformities, seizures, and developmental delay Lissencephaly (“Smooth Brain”) Absence of normal brain folds (gyri) Presents with severe developmental delay, intractable epilepsy Schizencephaly Clefts or splits in brain tissue Associated with motor weakness, seizures, intellectual disability Agenesis of Corpus Callosum Absence of the structure connecting the two hemispheres May result in seizures, coordination problems, and learning disabilities Porencephaly and Hydranencephaly Cystic cavities or absence of brain tissues due to intrauterine stroke or infections Polymicrogyria Excessive, abnormal small folds in the cerebral cortex Linked with epilepsy and motor impairment Dandy-Walker Malformation Cystic malformation of the posterior fossa with hydrocephalus Chiari Malformation with Syringomyelia Brain tissue extends into the spinal canal causing fluid-filled cysts and neurological deficits Megalencephaly or Microcephaly Abnormally large or small brain size at birth May be isolated or part of genetic syndromes Encephaloceles Brain herniation through skull defects, often visible at birth “These are rare, but for affected families, they are life-defining. Early diagnosis and individualized care offer the best hope.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman ⚠️ Symptoms Indicating a Possible Brain Malformation 🗣️ Delayed speech or inability to follow commands 🧒 Developmental delay or regression ⚡ Recurrent or intractable seizures 👁️ Visual and auditory processing problems 🧍 Abnormal head shape or head size (macro/microcephaly) 🚶 Poor balance, spasticity, or weakness of limbs 🧠 Ventricular enlargement or midline shift on imaging 🧪 Diagnostic Tools & Evaluation Strategy Dr. Nafaur Rahman uses the following approach for accurate evaluation: 🧲 MRI Brain with advanced sequences – Gold standard for detecting cortical malformations 🧠 Neurosonogram (for neonates) 🧬 Genetic testing if syndromic features are suspected 🧪 EEG – To detect epileptiform activity 📊 Neurodevelopmental assessments 🤝 Collaboration with geneticists, pediatricians, child neurologists, and rehabilitation experts 🛠️ Treatment and Neurosurgical Options While some congenital malformations require supportive care only, many benefit from surgical intervention, especially in cases with hydrocephalus, seizures, or mass effect. 1. Hydrocephalus Management Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt or Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV) for CSF diversion 2. Surgical Repair of Skull Defects Encephalocele repair with or without bone grafting or cranioplasty 3. Epilepsy Surgery Focal resection or hemispherectomy in selected severe epilepsy cases 4. Posterior Fossa Decompression For Chiari malformation with symptoms or syrinx 5. Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation Ongoing therapy for speech, motor, cognitive, and social development 🔁 Long-Term Outlook and Follow-Up Children with rare congenital brain disorders require: 👨⚕️ Lifelong neurological follow-up 🧠 Developmental monitoring and early intervention 🧘 Physiotherapy and occupational therapy 🗣️ Special education support 🧾 Periodic imaging and EEG (where epilepsy coexists) 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Bangladesh’s leading pediatric neurosurgeon with expertise in complex brain malformations 🏥 Based at the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) 🧒 Child-friendly care model at Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre ✅ Offers neurosurgical, diagnostic, and follow-up care under one roof 🧬 Collaborates with experts in genetics, neurology, neuro-rehabilitation 📞 Take Action Early – Optimize Your Child’s Neurological Potential Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointments: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com
Common Types