Sagittal Synostosis (Scaphocephaly)
Sagittal Synostosis (Scaphocephaly)
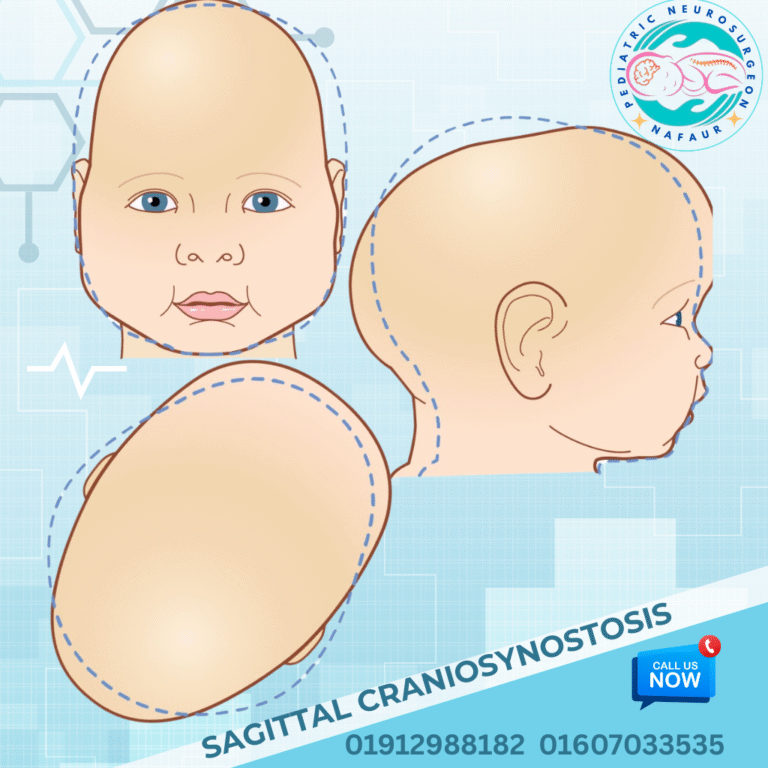
Sagittal synostosis, also known as scaphocephaly, is the most common type of craniosynostosis, a congenital condition characterized by the premature fusion of the sagittal suture — the fibrous joint running from the front to the back along the top midline of the skull. This early fusion restricts transverse skull growth and causes the head to elongate abnormally from front to back, resulting in a long, narrow, boat-shaped skull (hence “scaphocephaly” derived from Greek meaning “boat-shaped head”). This condition affects approximately 1 in 2000 to 3000 live births worldwide and is a significant cause of abnormal head shape and potential neurodevelopmental issues in children if left untreated. 🌍 Sagittal Synostosis in the Bangladesh Context In Bangladesh, awareness and timely diagnosis of sagittal synostosis remain limited, particularly in rural and underserved areas, due to: 🔬 Lack of widespread newborn screening and cranial imaging 👶 Misinterpretation of head shape abnormalities as normal variations 🏥 Limited access to pediatric neurosurgical expertise outside major cities 🩺 Delayed referral causing increased complexity in surgical correction 💊 Nutritional and prenatal care gaps contributing to congenital anomalies Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, a leading pediatric neurosurgeon in Bangladesh, specializes in early diagnosis and modern surgical management of sagittal synostosis, improving outcomes for affected children across the country. ⚠️ Causes and Risk Factors Premature fusion of the sagittal suture during fetal skull development Genetic mutations affecting skull growth and suture biology Maternal factors including poor nutrition, folic acid deficiency, and environmental exposures Occasionally associated with syndromes such as Crouzon or Apert syndrome, though most cases are isolated 🧒 Signs and Symptoms Elongated, narrow head shape with prominent forehead and occiput (back of head) Ridging along the sagittal suture felt on physical exam Increased head circumference in the anteroposterior dimension Possible frontal bossing (prominent forehead) and occipital prominence Delayed or impaired neurodevelopment in severe or untreated cases Rarely, increased intracranial pressure causing headaches, irritability, or vomiting 🔍 Diagnosis and Imaging Accurate diagnosis involves clinical examination and imaging studies: 🦴 X-rays of the skull can show premature suture fusion and skull shape 🧲 CT Scan with 3D reconstruction is the gold standard for detailed suture and cranial bone assessment 🧠 MRI may be used to evaluate brain development and rule out associated anomalies Comprehensive neurological and developmental assessments Genetic counseling if syndromic features are suspected 🛠️ Surgical Treatment Options The primary treatment is surgical correction, ideally performed between 3 to 6 months of age to optimize skull shape and brain development. Surgical Goals: Release fused sagittal suture to allow normal skull growth Reshape the skull to a more typical round contour Prevent or relieve intracranial hypertension Minimize blood loss and surgical morbidity using modern techniques Common Surgical Procedures: Strip Craniectomy Removal of the fused suture strip to allow natural skull remodeling Often combined with postoperative helmet therapy in younger infants Cranial Vault Remodeling More extensive reshaping of skull bones for older infants or severe deformities May involve fronto-occipital advancement and barrel stave osteotomies Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Surgery Less invasive option with smaller incisions and faster recovery Requires early diagnosis (within first 3 months) and helmet therapy 🏥 Postoperative Care and Follow-Up Hospital stay typically 3–5 days depending on procedure Pain management and infection prevention Follow-up CT scans or 3D photos to monitor skull growth Helmet therapy post-surgery when indicated Developmental surveillance and neurocognitive support Long-term multidisciplinary care with neurosurgeons, pediatricians, and rehabilitation therapists 🔄 Prognosis and Outcomes Most children experience excellent cosmetic and functional outcomes with early surgery Skull shape normalizes over time, reducing psychosocial impacts Early intervention minimizes risk of intracranial hypertension and neurodevelopmental delay Lifelong follow-up ensures continued neurological health and cognitive development 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Renowned pediatric neurosurgeon with specialized training in craniosynostosis surgery Operates at the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS), Dhaka Leader of Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre providing family-centered care Uses advanced imaging, surgical, and helmet therapy protocols tailored to Bangladesh’s needs Trusted by families nationwide for safe, expert management of complex pediatric skull disorders 📞 Schedule a Consultation for Sagittal Synostosis Today Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Call for appointments: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com