Coronal Synostosis ( Anterior Plagiocephaly)
Coronal Synostosis ( Anterior Plagiocephaly)
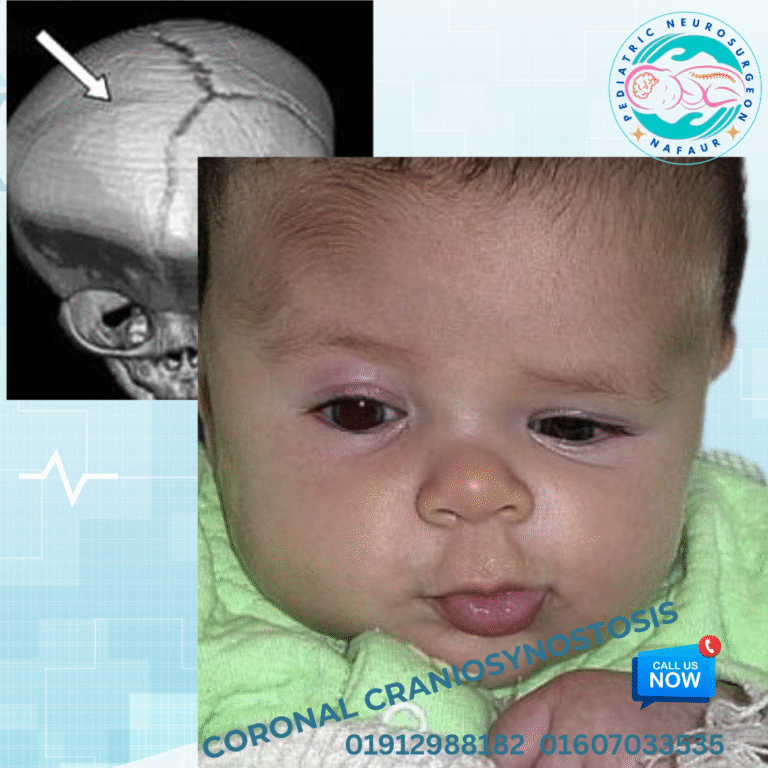
Coronal synostosis, also called anterior plagiocephaly, is a congenital cranial deformity caused by the premature fusion of one or both coronal sutures—the sutures running from ear to ear across the top front of the skull. This early fusion restricts skull growth perpendicular to the affected suture, leading to an asymmetric and uneven head shape. When only one coronal suture fuses early, it results in unilateral coronal synostosis, producing a characteristic flattening of the forehead on one side, elevation of the opposite eyebrow, and displacement of the ear. If both sutures fuse prematurely (bilateral coronal synostosis), the head becomes abnormally short from front to back and wide from side to side, sometimes associated with other craniofacial abnormalities. 🌍 Coronal Synostosis in the Bangladesh Context Limited awareness of craniosynostosis in many communities leads to delayed diagnosis and treatment Misconceptions often cause families to ignore abnormal head shapes or seek traditional remedies Access to pediatric neurosurgical care is mainly centralized in Dhaka, posing challenges for rural families Growing expertise at the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre is improving outcomes Early diagnosis and surgical intervention remain critical to avoid complications such as increased intracranial pressure and developmental delay ⚠️ Causes and Risk Factors Genetic mutations affecting cranial suture development Syndromic associations including Apert, Crouzon, or Muenke syndromes Environmental and maternal factors during pregnancy (e.g., folic acid deficiency, exposure to toxins) Sporadic and isolated premature fusion without known cause in many cases 🧒 Signs and Symptoms Noticeable asymmetry of the forehead and brow region (in unilateral cases) Flattening of the forehead on the affected side Elevated and bulging eyebrow on the opposite side Ipsilateral ear displaced anteriorly and downward Midface hypoplasia and orbital asymmetry (in severe or bilateral cases) Possible developmental delay or neurocognitive issues in untreated or syndromic cases Rare symptoms of increased intracranial pressure: headache, vomiting, irritability 🔍 Diagnosis and Imaging Detailed physical and neurological examination by pediatric neurosurgeon Skull X-rays showing fused coronal suture and characteristic skull deformity CT scan with 3D reconstruction provides precise bone anatomy and surgical planning MRI to assess brain structure and exclude other anomalies if developmental concerns exist Genetic testing if syndromic craniosynostosis is suspected 🛠️ Surgical Treatment Approaches Early surgical correction, ideally between 3 and 12 months of age, is essential to: Release the fused coronal suture Restore normal skull shape and symmetry Prevent or relieve elevated intracranial pressure Support normal brain growth and development Surgical Techniques Include: Open Cranial Vault Remodeling Removal and reshaping of affected bones to correct deformity Realignment of orbit and forehead contours Endoscopic Strip Craniectomy Minimally invasive option for selected infants diagnosed early Combined with postoperative helmet therapy for skull reshaping Fronto-Orbital Advancement For more severe or bilateral cases involving orbital correction 🏥 Postoperative Care and Follow-Up Hospital stay usually 5–7 days post-surgery Pain management and infection prevention protocols Regular neuroimaging follow-ups to assess skull remodeling Helmet therapy when indicated to assist skull reshaping Developmental assessments and early intervention programs Multidisciplinary approach including neurosurgery, pediatrics, physiotherapy, and speech therapy as needed 🔄 Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook Most children achieve excellent cosmetic and functional outcomes with timely surgery Early intervention reduces risk of intracranial hypertension and developmental delays Lifelong follow-up is recommended for syndromic patients or those with complex deformities Psychosocial benefits of improved appearance and neurological function are significant 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Leading pediatric neurosurgeon with expertise in craniosynostosis and complex craniofacial surgery Practices at National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS), Dhaka Heads multidisciplinary care at Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre Uses latest imaging, surgical techniques, and helmet therapy tailored to Bangladesh’s population Compassionate and family-centered care, guiding parents through diagnosis and treatment 📞 Contact for Expert Care on Coronal Synostosis (Anterior Plagiocephaly) Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Call for appointments: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com