Vein of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation
Vein of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation
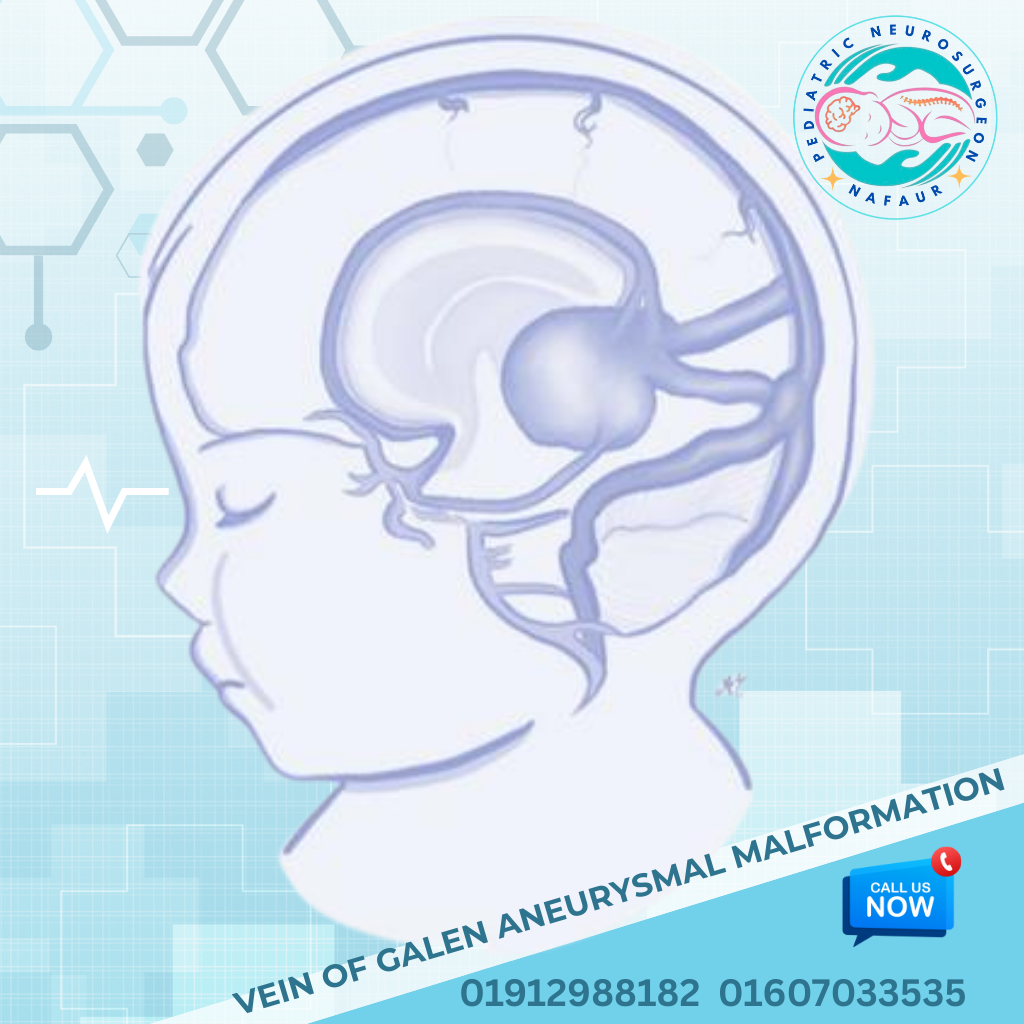
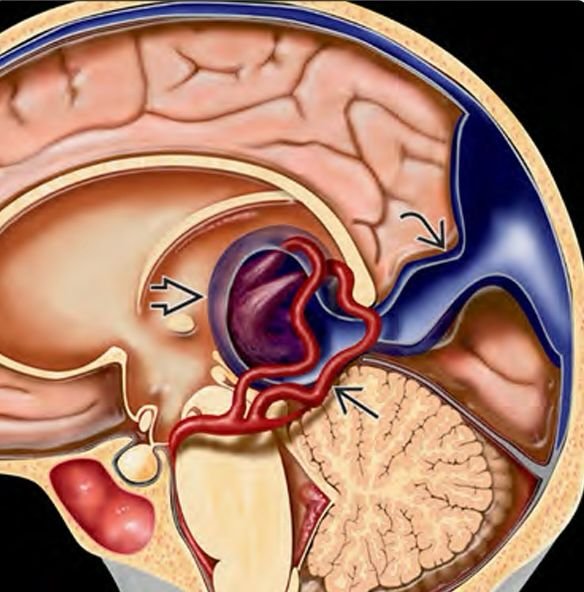
Vein of Galen Aneurysmal Malformation (VGAM) is a rare congenital vascular anomaly of the brain in which arteries abnormally connect to the median prosencephalic vein (an embryonic precursor to the vein of Galen), causing arteriovenous shunting. This high-flow malformation can lead to severe cardiac overload, hydrocephalus, seizures, and brain damage, particularly in newborns and infants. Unlike typical brain aneurysms, VGAM is not a true aneurysm but rather a developmental error in embryonic venous formation, often detected in utero or shortly after birth. Prompt diagnosis and early multidisciplinary intervention are essential to saving lives and improving neurological outcomes. In Bangladesh, cases of VGAM are often undetected until severe symptoms appear, due to limited prenatal imaging and lack of neonatal neurovascular awareness. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, one of the country's most experienced pediatric neurosurgeons, is a national leader in the diagnosis, treatment, and surgical management of VGAM. 🌍 The Bangladesh Perspective on VGAM Despite its rarity, VGAM is a critical condition that demands specialized care. In Bangladesh, VGAM presents unique challenges: 🧠 Limited antenatal neurosonography in rural and district health centers 👶 Neonatal heart failure misdiagnosed as congenital heart disease 🏥 Lack of awareness among pediatricians and neonatologists about VGAM 💉 Endovascular treatment access limited to major cities 💸 Families often face financial and logistic constraints To combat these issues, Dr. Nafaur Rahman has been pivotal in raising awareness, building treatment pathways, and performing surgical care for VGAM at both NINS and the Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre. ⚠️ Signs and Symptoms of VGAM in Infants and Children VGAM may manifest early in life or remain undiagnosed until complications develop: 👶 In Neonates: 💓 High-output cardiac failure unresponsive to medication 🧠 Hydrocephalus (enlarged head, bulging fontanelle) 🛌 Irritability, poor feeding, or drowsiness 💨 Fast breathing or respiratory distress 🩺 Enlarged liver or abnormal heart sounds 🧒 In Older Infants/Children: 🔁 Developmental delay ⚡ Seizures or epilepsy 👁️ Visual disturbances or nystagmus 🧏 Hearing loss (due to vascular compression) 🦵 Motor weakness or spasticity 🧠 Progressive macrocephaly or neurological decline “Many VGAM cases in Bangladesh are wrongly managed as heart disease until a brain scan reveals the truth. Early detection changes everything.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🧬 Causes and Types of VGAM VGAM is not hereditary but arises from abnormal vascular development during weeks 6–11 of gestation. 🔹 Two Main Types: Choroidal VGAM – Multiple arterial feeders from the anterior circulation; presents early in neonates with heart failure. Mural VGAM – Fewer, localized feeders; may present later in infancy or early childhood. Understanding the type helps guide treatment strategy and prognosis. 🏥 Diagnostic Evaluation at NINS & BP Neurocare Centre Dr. Nafaur Rahman’s centers offer specialized neonatal and pediatric neurodiagnostic services, including: 🔍 Diagnostic Tools: Prenatal Ultrasound & Fetal MRI – May detect VGAM in the third trimester Postnatal Transfontanellar Ultrasound – Initial bedside assessment MRI/MRA Brain – Gold standard for anatomical mapping CT Angiography (CTA) – Fast assessment in emergencies Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) – For pre-surgical planning Echocardiography – Assesses cardiac function due to AV shunting EEG – If seizures are present 🛠️ Treatment Options for Pediatric VGAM Successful treatment depends on early diagnosis, multidisciplinary teamwork, and timely endovascular or surgical intervention. 🔧 Primary Treatment: Endovascular Embolization Minimally invasive procedure via catheter to block abnormal vessels Performed in staged sessions to reduce shunt flow gradually Reduces risk of brain damage and heart failure Done under general anesthesia with pediatric neuro-interventionists 🧠 Surgical Management (In Select Cases): Needed if endovascular therapy is incomplete or not feasible Includes CSF diversion procedures like VP shunt in hydrocephalus May involve decompression or craniotomy for bleeding or mass effect “A multidisciplinary approach combining neurosurgery, interventional neuroradiology, neonatology, and pediatric cardiology is the key to VGAM survival.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🔁 Post-Treatment Recovery & Long-Term Care Dr. Nafaur ensures comprehensive long-term monitoring, including: 📅 Regular neuroimaging (MRI/DSA) to assess occlusion 🗣️ Speech and motor therapy for developmental support 🏫 Neurocognitive evaluation and academic follow-up 🧬 Genetic counseling if VGAM is part of a wider syndrome (rare) 💬 Family counseling and support groups 🚨 What Happens if VGAM Is Left Untreated? 💓 Severe, untreatable heart failure in neonates 🧠 Permanent brain damage due to prolonged high blood flow 🧑🦽 Developmental disability and spasticity ⚰️ Death from hemorrhage or cardiac decompensation In Bangladesh, mortality rates from untreated VGAM are high—prompt diagnosis and referral are essential to saving lives. 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman for VGAM Management? 🧠 Bangladesh’s leading pediatric neurosurgeon for complex vascular malformations 💉 Experienced in coordinating endovascular and surgical treatments for VGAM 🏥 Practices at NINS, equipped with neonatal ICU and advanced neuroimaging 🤝 Provides family-centered care with 24/7 support and follow-up 🎯 Focused on improving long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes for infants 📞 Contact for VGAM Evaluation or Referral Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com