Cerebral AVM
Cerebral AVM
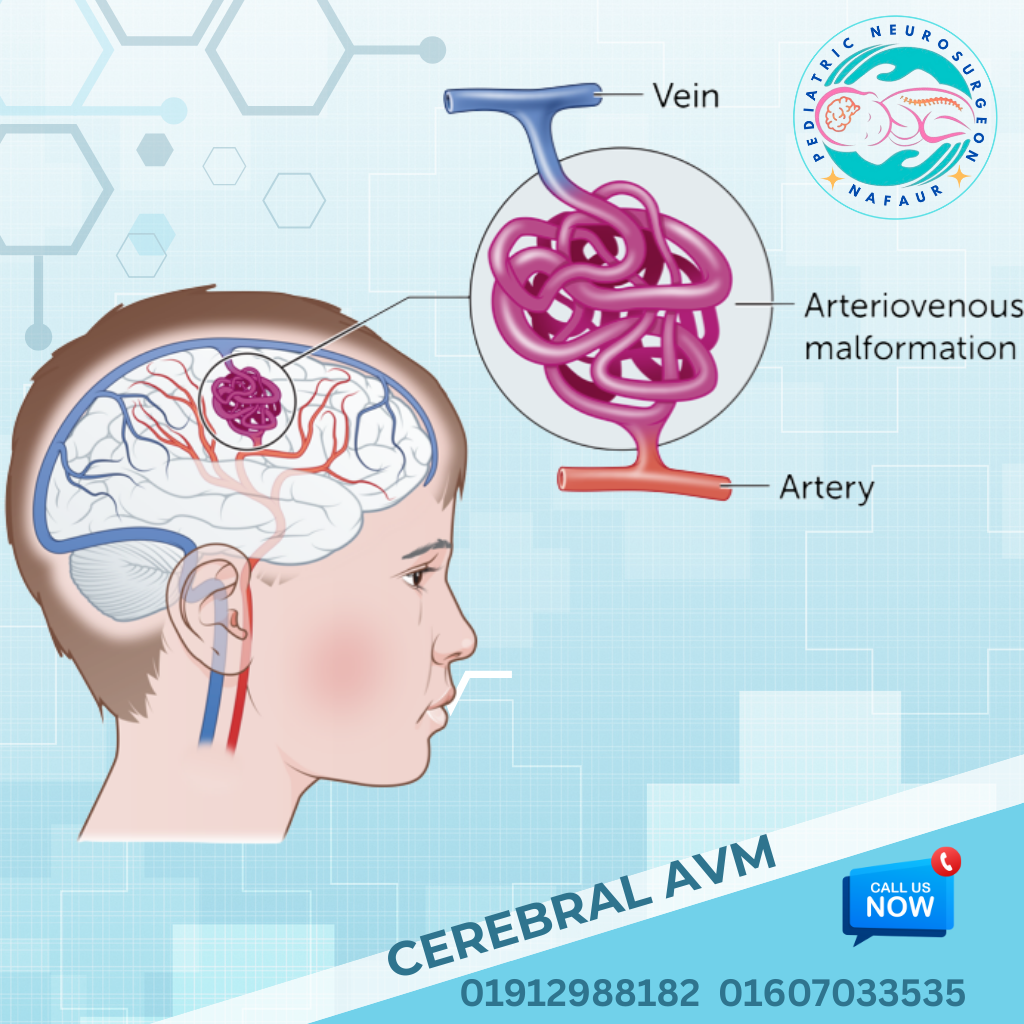
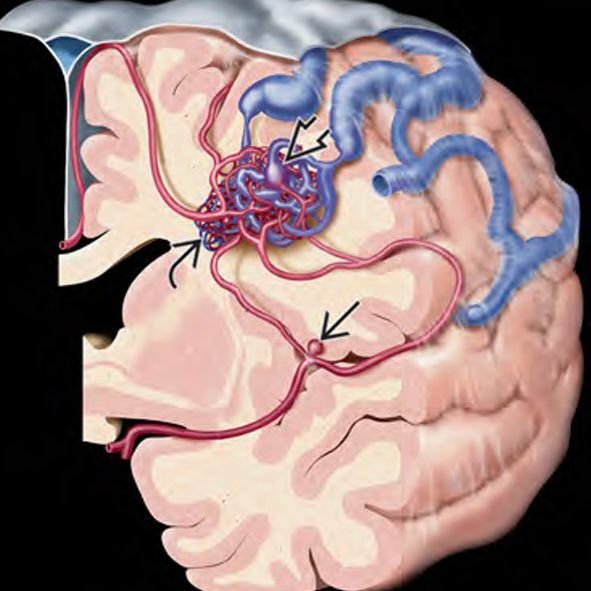
Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) are rare but serious vascular abnormalities where arteries connect directly to veins without the normal capillary network, creating high-pressure blood flow in the brain. This can lead to intracranial hemorrhage, seizures, headaches, and neurological deficits in children. While AVMs are often congenital, they may remain silent until a rupture occurs, usually during childhood or adolescence. In Bangladesh, delayed diagnosis and lack of access to pediatric vascular neurosurgeons often result in severe complications. However, with advancements in microsurgery, endovascular techniques, and neuroimaging, early treatment offers excellent outcomes. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman is one of Bangladesh’s few pediatric neurosurgeons trained in the complex management of AVMs in children, offering both life-saving surgical interventions and long-term neurological recovery plans. 🌍 Cerebral AVMs in Children: The Bangladesh Perspective In Bangladesh, most pediatric AVM cases come to attention only after rupture, resulting in: 🧠 Sudden intracerebral hemorrhage or stroke-like symptoms ⚡ Recurrent seizures misdiagnosed as epilepsy ❌ Lack of early neuroimaging due to cost or location 🏥 Limited awareness among general pediatricians or school health programs 💸 Financial barriers to advanced diagnostics or surgery Dr. Nafaur Rahman addresses these gaps by providing affordable and early surgical management at NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre, supported by neurovascular imaging and multidisciplinary pediatric teams. ⚠️ Symptoms of Pediatric Cerebral AVMs Many AVMs are silent until they bleed, but common symptoms include: 🩸 Sudden severe headache (sign of bleeding) ⚡ Seizures or epilepsy, especially in previously healthy children 🦵 Weakness or numbness in arms or legs 🧍 Loss of balance or gait disturbances 🧠 Fainting or loss of consciousness 🗣️ Speech problems or visual changes 🥱 Fatigue, cognitive decline, or personality changes “A single seizure in a previously normal child should never be ignored. It may be the only warning sign of a life-threatening AVM.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🧬 Causes and Risk Factors 🔹 Congenital abnormality of blood vessels during fetal development 🔹 May be sporadic or part of genetic syndromes (e.g., HHT) 🔹 Family history of AVMs or vascular malformations (rare) 🔹 AVMs can be found in both supratentorial and posterior fossa regions 🏥 Diagnosis at NINS & BP Neurocare Centre Early and accurate diagnosis is essential to prevent AVM rupture and permanent damage. Dr. Nafaur and his team utilize advanced tools such as: 🔍 Key Diagnostic Modalities: MRI with MR Angiography (MRA) – First-line, non-invasive detection tool CT Angiography (CTA) – Useful for emergency bleeds Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) – Gold standard for surgical planning EEG – For AVMs presenting with seizures Neurocognitive evaluation – If academic or behavioral issues are present 🛠️ Treatment & Surgical Management of AVMs The goal is to remove or eliminate the AVM before it ruptures or causes further neurological damage. Treatment depends on: AVM location, size, and Spetzler-Martin grade Presence of hemorrhage or seizures Child’s age, neurological status, and overall health ✅ Treatment Options Offered by Dr. Nafaur Rahman: 🧠 Microsurgical Resection Preferred in accessible, low-grade AVMs Offers complete cure if total excision is achieved Performed with neuronavigation and intraoperative monitoring 💉 Endovascular Embolization Minimally invasive technique using a catheter to block blood flow to AVM Often used before surgery to reduce bleeding risk May be used alone in selected cases ⚛️ Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) Option for deep-seated or inoperable AVMs Uses focused radiation to close abnormal vessels over 1–3 years Not readily available in many regions of Bangladesh “Microsurgical AVM resection in children is highly rewarding. With complete removal, children can enjoy a seizure-free, stroke-free life.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🔁 Post-Treatment Care & Follow-Up 🧠 MRI/MRA every 6–12 months to monitor recurrence or residual AVM ⚕️ Antiepileptic medication for seizure control post-treatment 🧒 Neurorehabilitation for motor, speech, and cognitive development 🏫 Academic and psychological support for reintegration 📊 Family screening in suspected familial AVMs or syndromes 🚨 Complications if Left Untreated 🩸 Recurrent brain hemorrhages ⚡ Intractable epilepsy 🚫 Cognitive decline and academic failure 🧑🦽 Permanent neurological disability or paralysis ⚰️ Death from massive intracranial bleeding 🧒 Dr. Nafaur Rahman’s Pediatric AVM Initiative in Bangladesh 🏥 Introduced child-specific AVM treatment protocols at NINS 👨👩👧 Educates parents and pediatricians about early warning signs 💬 Trains junior neurosurgeons in safe AVM resection techniques 📈 Leads awareness campaigns on pediatric brain stroke and seizures 💸 Offers subsidized treatment options for financially struggling families 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 One of Bangladesh’s top experts in pediatric neurovascular surgery 🎯 Specialized in AVM management using microsurgery and embolization 🏥 Practices at National Institute of Neurosciences (NINS) and BP Neurocare Centre 🧒 Uses child-friendly anesthesia, minimal blood loss, and rapid recovery techniques 🤝 Trusted by parents across Bangladesh for accurate diagnosis, compassionate care, and long-term support 📞 Contact for Pediatric AVM Consultation, Diagnosis, or Surgery Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com