Cerebral Aneurysm
Cerebral Aneurysm
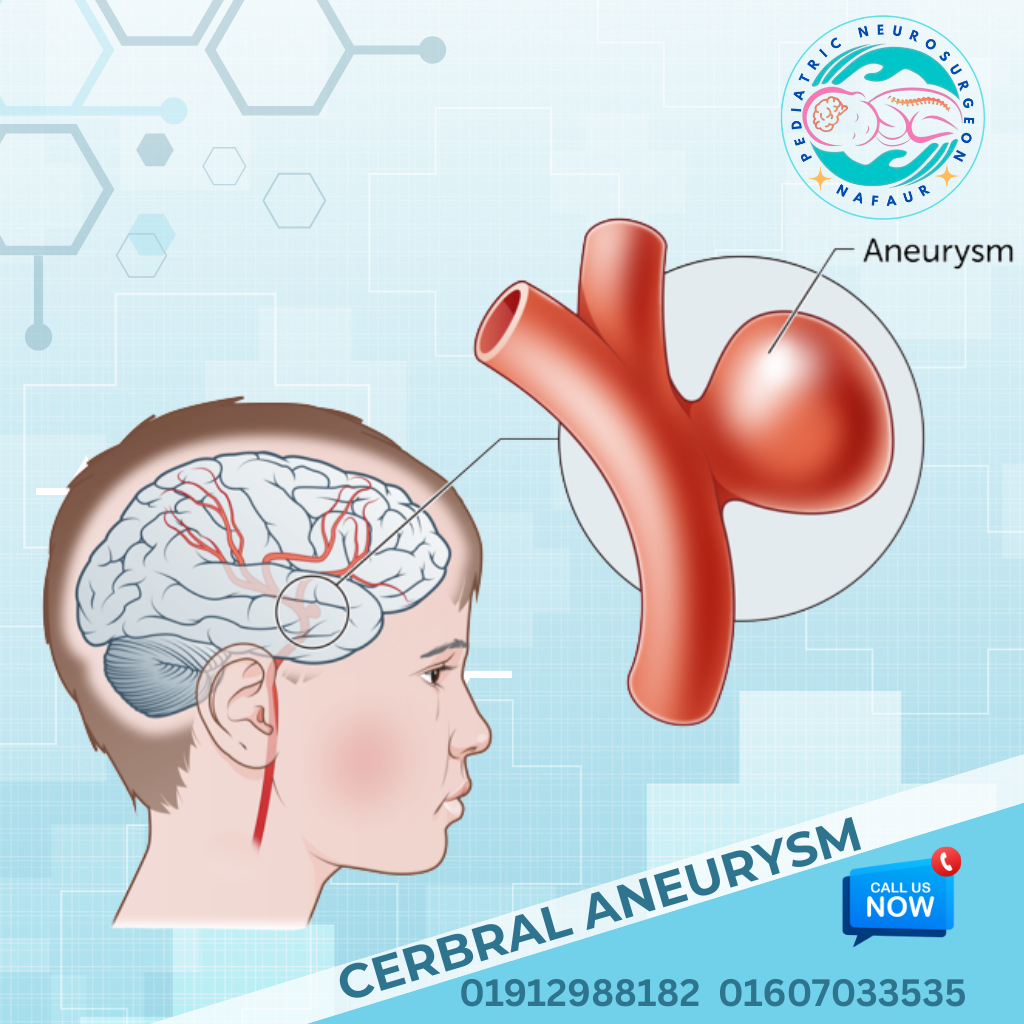
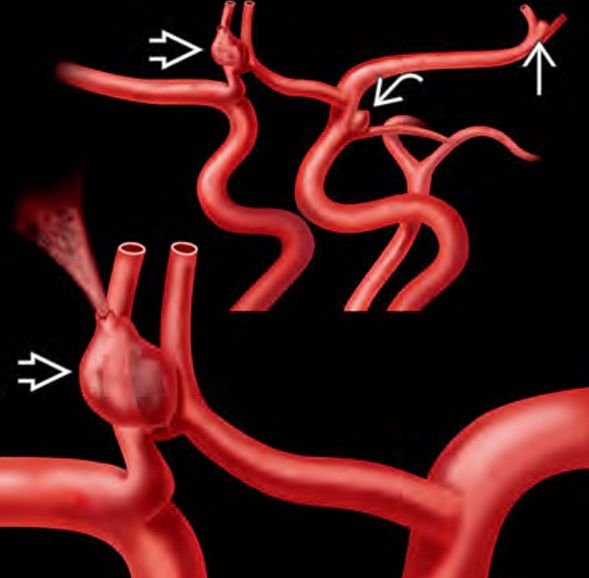
A Pediatric Cerebral Aneurysm is a rare but life-threatening vascular condition in which a weak spot in a cerebral artery balloons or bulges, increasing the risk of rupture and brain hemorrhage. Though far less common than in adults, aneurysms in children are often larger, more likely to bleed, and may be associated with congenital vascular disorders or infections. In the Bangladeshi context, due to limited awareness and diagnostic accessibility, many pediatric cerebral aneurysms are detected only after rupture, leading to high morbidity and mortality. Early identification and intervention by pediatric neurosurgical experts like Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman can prevent devastating outcomes and preserve the child’s quality of life. 🌍 Pediatric Cerebral Aneurysms in the Bangladesh Perspective Pediatric cerebral aneurysms are underdiagnosed and frequently mismanaged in Bangladesh due to: 🧠 Lack of routine neuroimaging in children with headaches or seizures ⏱️ Delayed referral to neurosurgeons in rural settings ❌ Misconceptions that aneurysms only occur in adults 🩸 Children presenting late with ruptured aneurysms and hydrocephalus 💰 Cost constraints for imaging like DSA or MRA Dr. Nafaur Rahman, a leading figure in pediatric neurosurgery, is actively addressing these gaps through clinical excellence, affordable surgical care, and community-level advocacy across Bangladesh. ⚠️ Signs & Symptoms of Brain Aneurysms in Children Symptoms may vary based on whether the aneurysm is ruptured or unruptured: 🔴 Symptoms of Ruptured Aneurysm (Medical Emergency): Sudden, explosive headache (“worst headache of life”) Vomiting and nausea Seizures or loss of consciousness Neck stiffness Visual disturbances or double vision Weakness or paralysis Drowsiness or coma in severe cases 🟠 Symptoms of Unruptured Aneurysm: Persistent, localized headaches Vision problems Hearing loss (in posterior circulation aneurysms) Facial pain or cranial nerve palsy Seizures without other cause Developmental delay in infants (rare cases with large aneurysms) “Children are not immune to aneurysms. A single unexplained seizure or severe headache may be the only early clue. Timely neuroimaging saves lives.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🧬 Causes & Risk Factors in Pediatric Aneurysms In Bangladesh, pediatric aneurysms may result from: 🔹 Congenital vascular defects (arterial wall abnormalities) 🔹 Genetic disorders – such as Ehlers-Danlos or polycystic kidney disease 🔹 Infections (mycotic aneurysms) from bacterial endocarditis 🔹 Head trauma – especially in infants or toddlers 🔹 High blood pressure or vascular inflammation 🔹 Family history of cerebral aneurysms 🏥 Diagnostic Protocol at NINS & Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre Timely and accurate diagnosis is key to preventing rupture or rebleeding. Dr. Nafaur Rahman’s centers offer advanced, child-friendly imaging techniques: 🧪 Key Diagnostic Tools: MRI Brain + MRA (Magnetic Resonance Angiography) – First-line, non-invasive CT Angiography (CTA) – Helpful in emergency cases Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA) – Gold standard for detailed vascular mapping Lumbar puncture – If subarachnoid hemorrhage is suspected but imaging is inconclusive 3D Reconstructions – For surgical planning in complex aneurysms All tests are conducted with minimal discomfort and sedation protocols appropriate for children. 🛠️ Treatment Options for Pediatric Cerebral Aneurysms Treatment depends on aneurysm size, location, status (ruptured/unruptured), and child’s neurological condition. ✅ Non-Surgical Management (Observation): Small, asymptomatic aneurysms in inaccessible regions Serial imaging every 6–12 months Strict blood pressure control and infection prevention 🔧 Surgical and Endovascular Interventions by Dr. Nafaur Rahman: Microsurgical Clipping A permanent clip is placed across the neck of the aneurysm Preferred in large, ruptured, or accessible aneurysms Offers long-term cure and low recurrence Endovascular Coiling (via DSA) A catheter is threaded into the aneurysm to fill it with platinum coils Minimally invasive with shorter recovery Suitable for deep-seated aneurysms or children with comorbidities Bypass Surgery or Wrapping For complex aneurysms not amenable to clipping or coiling Involves creating an alternate blood flow pathway “Surgical success in children relies on preserving development, not just curing disease. Every decision balances safety and long-term potential.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🔁 Postoperative Care & Long-Term Monitoring Children treated for cerebral aneurysm require lifelong follow-up and family education: Regular MRA/DSA scans for recurrence or new aneurysm formation Neurocognitive assessment and school re-integration Seizure control if required Speech or motor therapy after brain hemorrhage recovery Family genetic screening if hereditary component is suspected 🚨 Risks of Untreated Pediatric Aneurysms Without proper diagnosis or treatment, a cerebral aneurysm can lead to: 🩸 Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) ⚡ Intractable seizures 🧠 Brain swelling and herniation 🧑🦽 Permanent disability or paralysis ⚰️ Sudden death, particularly with posterior circulation rupture 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Among the few in Bangladesh performing complex pediatric aneurysm surgeries 🏥 Practices at National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) 🧒 Uses minimally invasive techniques, tailored for children 🩺 Trained in both microsurgical and endovascular aneurysm management 👫 Empathetic, child- and parent-focused care with lifelong follow-up plans 📞 Contact for Pediatric Aneurysm Consultation or Surgery Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com