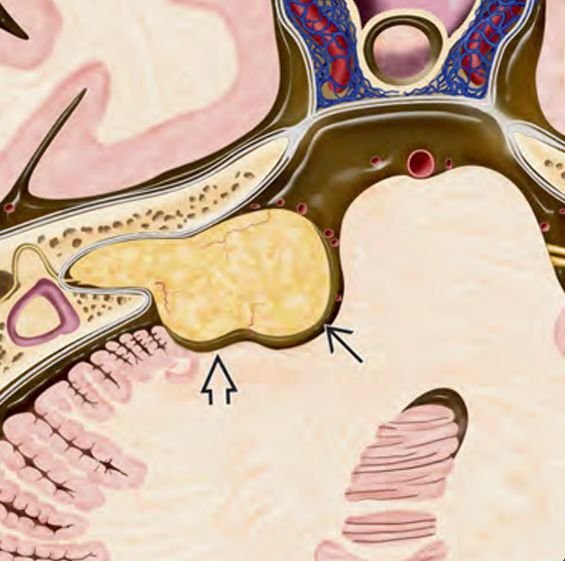
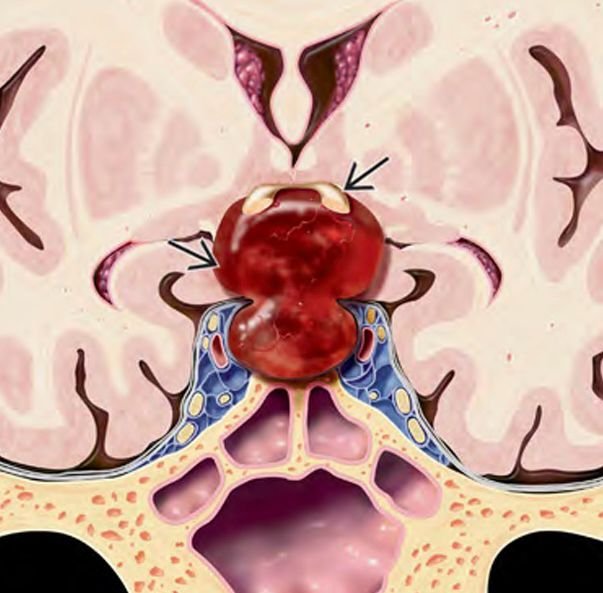
Sarcomas
Sarcomas
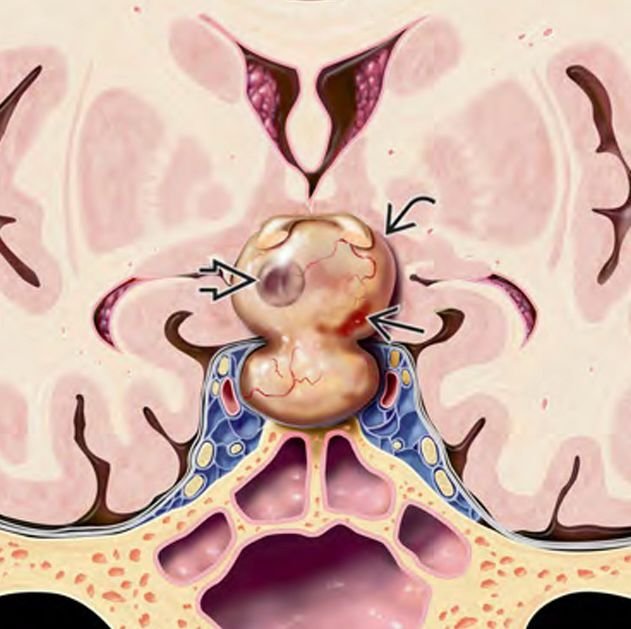
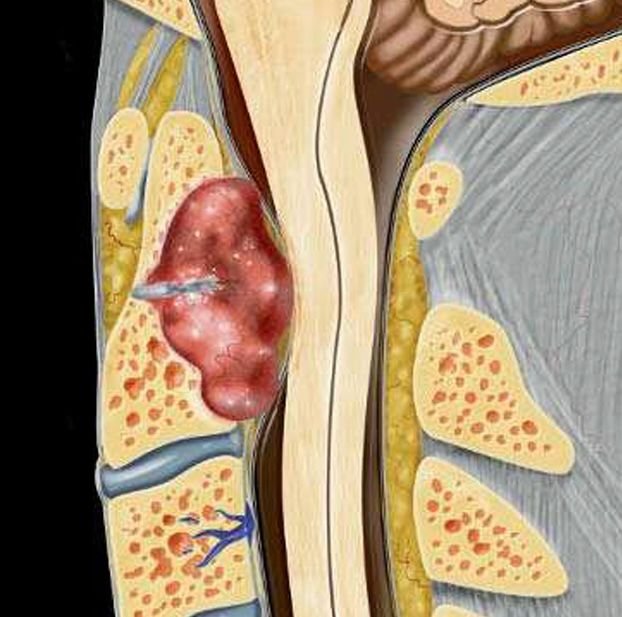
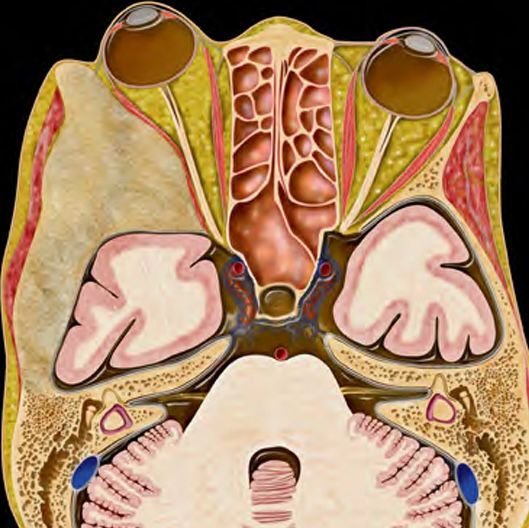
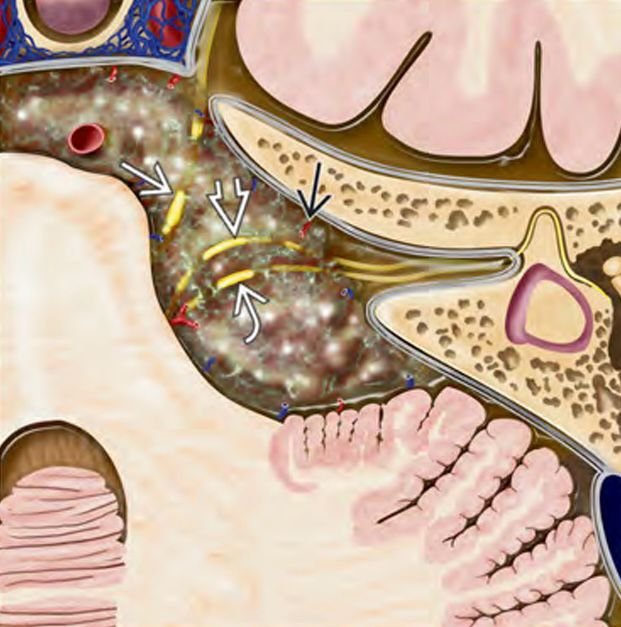
Pediatric skull base sarcomas are rare, aggressive malignant tumors originating from the connective tissues, bone, cartilage, or soft tissues located at the base of the skull. These sarcomas pose significant challenges due to their proximity to critical neurovascular structures, complex anatomy, and often advanced presentation at diagnosis. In Bangladesh, the management of these rare tumors requires specialized pediatric neurosurgical expertise combined with multidisciplinary oncology care to achieve the best possible outcomes. Under the leadership of Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, children receive cutting-edge surgical treatment, supported by chemotherapy and radiotherapy protocols adapted for the pediatric population. Epidemiology and Importance in Bangladesh Though sarcomas comprise a small fraction of pediatric skull base tumors, they are among the most malignant and life-threatening lesions. Common subtypes include Ewing sarcoma, osteosarcoma, chondrosarcoma, and rhabdomyosarcoma. Due to limited awareness and diagnostic resources across Bangladesh, many children are diagnosed at advanced stages, emphasizing the need for early referral and specialized care. Centers like the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre are pivotal in improving access to timely diagnosis and comprehensive management for pediatric patients nationwide. Causes and Pathophysiology Originate from mesenchymal tissues including bone, cartilage, and muscle precursors at the skull base Genetic mutations and environmental factors may contribute, although exact causes often remain unknown Sarcomas are characterized by rapid growth, local invasion, and potential for distant metastasis Skull base involvement complicates treatment due to adjacent vital structures including cranial nerves, brainstem, and major vessels Clinical Presentation Symptoms depend on tumor size and location and may include: Persistent headaches Facial swelling or deformity Cranial nerve palsies causing facial weakness, hearing loss, swallowing difficulties, or vision changes Nasal obstruction or epistaxis if tumor involves sinonasal region Difficulty in balance or coordination due to brainstem or cerebellar compression Rapidly progressive symptoms are common in aggressive sarcomas Early symptoms are often subtle, leading to delayed diagnosis. Diagnostic Approach Imaging MRI with contrast provides detailed assessment of tumor extent, neurovascular involvement, and brain invasion CT scan assists in evaluating bony destruction and calcifications PET-CT scan for staging and detecting metastatic disease Histopathology Biopsy under image guidance or surgical approach is essential for definitive diagnosis Immunohistochemistry and molecular studies help subtype sarcomas for targeted therapy Other Evaluations Complete neurological and cranial nerve examination Assessment for regional lymph node involvement Multidisciplinary tumor board discussion for treatment planning Treatment Modalities Surgery Maximal safe resection is the cornerstone of treatment Skull base surgical approaches are customized based on tumor location: Endoscopic endonasal approaches for midline tumors Open microsurgical approaches for lateral or extensive tumors Goal is complete tumor removal while preserving neurological function Dr. Nafaur Rahman employs advanced microsurgical techniques, neuronavigation, and intraoperative neuromonitoring to optimize outcomes Chemotherapy Integral for sarcoma treatment, especially Ewing sarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma Administered before surgery (neoadjuvant) or after surgery (adjuvant) to control systemic disease Radiotherapy Used as adjuvant therapy to improve local control Precision radiotherapy techniques minimize damage to developing brain tissue Prognosis and Follow-up Prognosis depends on tumor subtype, extent at diagnosis, surgical resection completeness, and response to adjuvant therapies Early-stage tumors treated with multimodal therapy have improved survival rates Regular long-term follow-up with imaging is critical to detect recurrence or metastasis early Challenges in Bangladesh Limited pediatric oncology and neurosurgical facilities in many regions Delayed presentation due to lack of awareness and access to specialized care Financial and logistic constraints for comprehensive multimodal therapy Necessity of centralized multidisciplinary care at centers like NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Specialized expertise in pediatric skull base sarcoma surgery Experience with multimodal treatment planning in collaboration with pediatric oncology teams Access to modern surgical technologies including neuronavigation, endoscopy, and intraoperative monitoring Dedicated to delivering compassionate, affordable, and family-centered care in Bangladesh Proven track record of managing complex pediatric neuro-oncological cases with positive outcomes Contact Information Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Serial & Appointment: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com