Pituitary Adenomas (in adolescents)
Pituitary Adenomas (in adolescents)
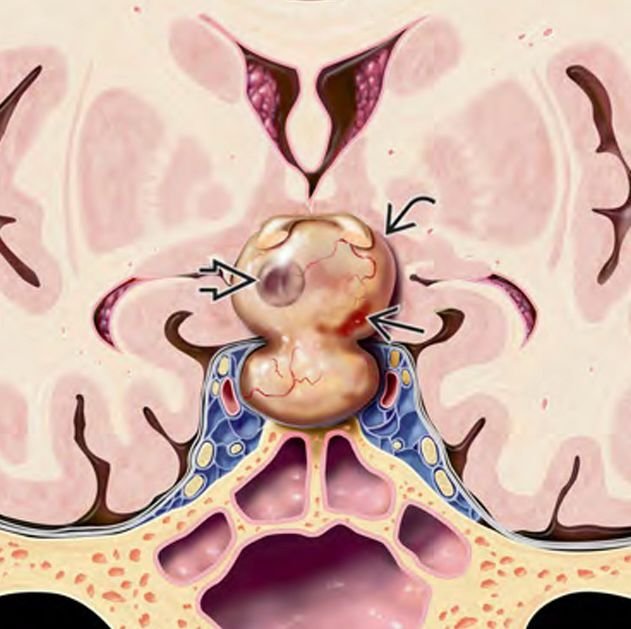
Pituitary adenomas are benign tumors that arise from the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain within a bony structure called the sella turcica. Though commonly seen in adults, these tumors may also appear in adolescents, causing hormonal disturbances, visual problems, and growth abnormalities. They can either be functioning (hormone-secreting) or non-functioning (non-secreting). In adolescents, early diagnosis and expert neurosurgical intervention can reverse many symptoms and restore normal development. In Bangladesh, increasing awareness and timely access to pediatric neurosurgeons like Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman is vital to managing pituitary tumors effectively. 🌍 Pituitary Tumors in Bangladesh: Why They Are Often Missed In Bangladesh, many adolescents with pituitary adenomas are misdiagnosed or undiagnosed for years due to lack of awareness and access to endocrine testing or MRI scans. Symptoms such as irregular menstruation, excessive height gain, galactorrhea (milk discharge from breasts), or visual issues are frequently misattributed to general puberty-related changes or eye problems. Dr. Nafaur Rahman and his team at NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre specialize in neuroendocrine tumor evaluation, using advanced imaging, hormone panels, and endoscopic neurosurgical techniques to manage these tumors successfully in teenagers. 🧬 Types of Pituitary Adenomas in Adolescents Prolactinomas Most common type in adolescents Cause excess prolactin production Symptoms: Delayed puberty, irregular menstruation, breast discharge, infertility Growth Hormone-Secreting Adenomas (Somatotroph Adenomas) Cause gigantism in adolescents Features: Excessive growth of hands, feet, jaw; joint pain; headaches Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)-Secreting Adenomas Cause Cushing's disease Features: Weight gain, moon face, thin skin, stretch marks Non-Functioning Pituitary Adenomas Do not produce hormones Present with headache, visual loss, and pituitary insufficiency 🧒 Common Symptoms in Adolescents Headaches, especially morning headaches Visual disturbances, including peripheral vision loss or blurry vision Irregular periods or absence of menstruation (amenorrhea) Milky breast discharge in girls and boys Delayed or early puberty Abnormal height gain or stunted growth Weight changes or facial swelling Fatigue, weakness, depression Seizures or vomiting in large tumors These symptoms often go unnoticed or untreated in many parts of Bangladesh, especially in rural and suburban areas where pediatric endocrinology services are limited. 🔍 Diagnosis of Pituitary Adenoma 🧠 Imaging MRI Brain with Pituitary Protocol: Gold standard Detects tumor size, shape, and optic chiasm involvement Differentiates between microadenomas (10 mm) 🧪 Hormonal Blood Tests Prolactin level Growth hormone and IGF-1 ACTH and cortisol levels TSH, LH, FSH, estrogen/testosterone levels 👁️ Visual Field Testing Essential to assess pressure on optic chiasm 🛠️ Treatment Options ✂️ 1. Surgical Removal Primary treatment for macroadenomas and functioning tumors Endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery is preferred—minimally invasive, safe, with short recovery Dr. Nafaur Rahman is highly skilled in endonasal approaches, using neuro-navigation and intraoperative imaging for precision 💊 2. Medical Management Prolactinomas often respond to dopamine agonists (e.g., cabergoline, bromocriptine) Monitored through serial hormone levels and MRI ☢️ 3. Radiotherapy Used in incomplete resections, recurrences, or aggressive adenomas Stereotactic radiosurgery or IMRT may be considered 🔄 Long-Term Follow-Up Regular MRI scans every 6–12 months Hormone testing to monitor pituitary function Endocrinology consultation for hormonal replacement if needed Ophthalmology follow-up for visual improvement or preservation 🧭 Prognosis Excellent prognosis with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment Most adolescents resume normal schooling, growth, and development Hormonal normalization possible in most functioning adenomas Visual symptoms often reversible if treated early Multidisciplinary follow-up ensures better long-term outcomes ⚠️ Complications of Delayed Diagnosis Permanent hormonal deficiency (hypopituitarism) Vision loss due to prolonged optic nerve compression Psychological issues, poor academic performance, social isolation Infertility or delayed sexual development Increased tumor size leading to complex surgery 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? One of the leading pediatric neurosurgeons in Bangladesh Expert in endoscopic transsphenoidal surgery for pituitary tumors Collaborates with endocrinologists, radiologists, and pediatricians for complete care Provides affordable, specialized care at NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre Focuses on patient safety, long-term outcomes, and family education 📞 Book Your Appointment Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Serial & Appointment: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com