Meningiomas
Meningiomas
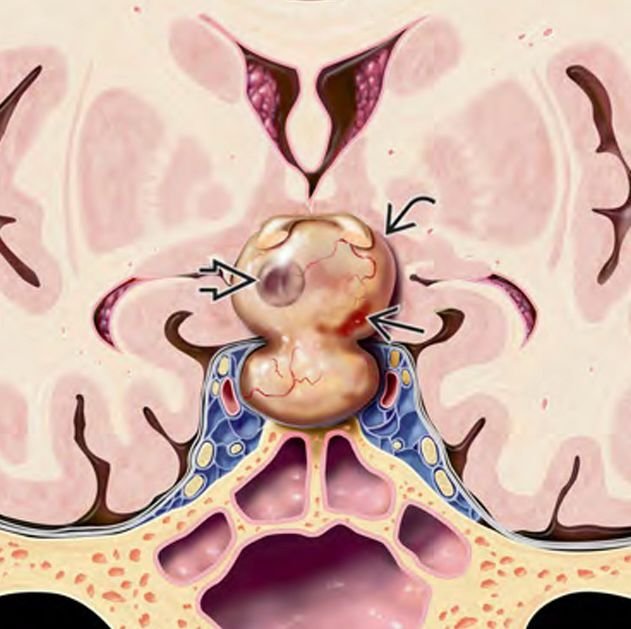
Meningiomas are tumors that arise from the meninges, the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. While meningiomas are more common in adults, they can also occur in children, particularly at the skull base — a complex anatomical region where the brain meets the bones of the head and face. Pediatric skull base meningiomas are rare but often challenging due to their proximity to vital nerves and blood vessels. In Bangladesh, timely diagnosis and specialized surgical treatment are essential for these tumors to prevent serious neurological deficits. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman offers advanced expertise in managing these rare tumors, combining modern neurosurgical techniques with a multidisciplinary approach tailored for children. Epidemiology and Importance in Bangladesh Pediatric meningiomas represent less than 5% of all childhood brain tumors but tend to be more aggressive and complex when located at the skull base. Due to limited awareness and diagnostic resources in many parts of Bangladesh, these tumors are often detected late, increasing the risks associated with treatment. Children presenting with symptoms such as persistent headaches, vision problems, or cranial nerve dysfunction should be evaluated by pediatric neurosurgical specialists for early detection. Facilities like NINS and the Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre are at the forefront of offering specialized care in Bangladesh. Causes and Risk Factors Arise from arachnoid cap cells in the meninges Can be associated with genetic conditions like Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) Exposure to radiation may increase risk, although rare in children Skull base location involves areas such as the clivus, cavernous sinus, sphenoid wing, and petroclival region Clinical Presentation Symptoms depend on tumor size, location, and involved nerves: Headaches — often persistent and worsening Visual disturbances — double vision, loss of visual fields, or decreased acuity Cranial nerve palsies causing facial weakness, numbness, hearing loss, or swallowing difficulty Balance and coordination problems if brainstem or cerebellum affected Seizures (less common in skull base tumors) Behavioral changes or developmental delay in some children Due to the subtle onset, symptoms in children may be overlooked or attributed to common pediatric illnesses. Diagnostic Approach Imaging Studies MRI with contrast is the gold standard to define tumor size, extent, and relation to critical structures CT scan helps identify bone involvement and calcifications MR Angiography to evaluate blood vessel displacement or encasement Other Evaluations Detailed neurological and cranial nerve examination Visual field testing by ophthalmology Genetic testing in suspected NF2 cases Treatment Modalities 1. Surgical Resection The mainstay of treatment for skull base meningiomas Surgical approach depends on tumor location and size, requiring advanced skull base techniques: Transcranial approaches (e.g., frontotemporal, subtemporal, or retrosigmoid) Endoscopic endonasal surgery for select midline tumors Goal: Maximal safe resection preserving neurological function Dr. Nafaur Rahman uses microsurgical techniques, neuronavigation, and intraoperative monitoring for precise tumor removal and nerve preservation 2. Radiotherapy Used as adjuvant therapy for residual, recurrent, or inoperable tumors Techniques such as stereotactic radiosurgery or fractionated radiotherapy Cautious use in children due to potential long-term side effects 3. Multidisciplinary Support Pediatric neurology, endocrinology, ophthalmology, and rehabilitation services for comprehensive care Long-term follow-up with serial imaging and neurological assessment Prognosis and Follow-up Pediatric skull base meningiomas tend to have higher recurrence rates than adult tumors Prognosis depends on extent of resection, tumor grade, and location Early surgical intervention improves outcomes and reduces morbidity Lifelong follow-up is recommended to monitor for recurrence or delayed complications Challenges in Bangladesh Limited availability of specialized skull base neurosurgical services for children outside major cities Delays in diagnosis due to lack of awareness among healthcare providers and families Financial constraints limiting access to advanced imaging and treatment Need for expanding pediatric neurosurgery expertise and infrastructure at centers like NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Experienced pediatric neurosurgeon specialized in complex skull base tumor surgeries Access to cutting-edge neurosurgical tools including neuronavigation, intraoperative monitoring, and endoscopy Collaborative care model involving multiple specialties to optimize child health outcomes Commitment to affordable, high-quality care tailored to the needs of Bangladeshi children and families Contact Information Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Serial & Appointment: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com