Craniopharyngioma
Craniopharyngioma
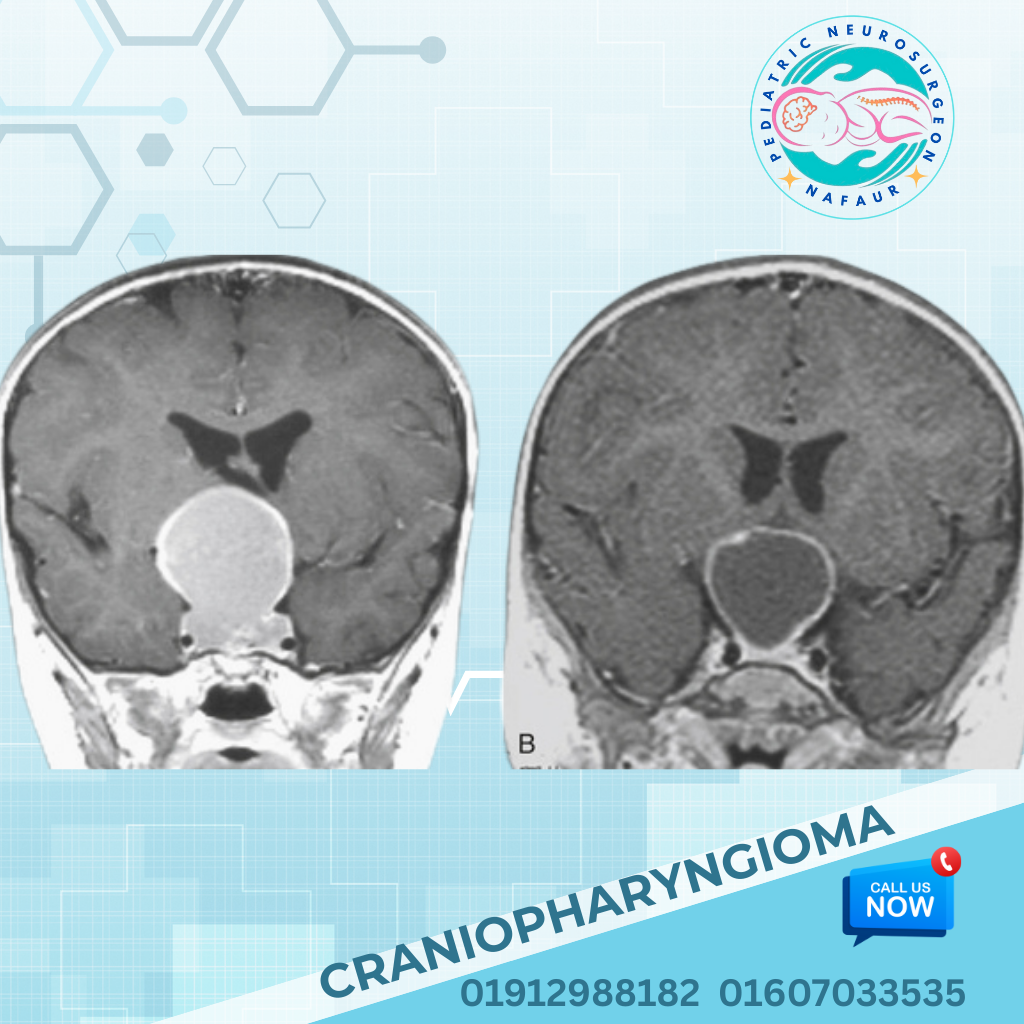
Craniopharyngioma is a rare, benign (non-cancerous) but locally aggressive brain tumor that most commonly occurs in children aged 5 to 14 years. Originating near the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, it grows in the sellar or suprasellar region of the brain, which controls hormonal balance, growth, vision, and emotions. Though not cancerous, craniopharyngiomas can be life-altering due to their strategic location, which may affect critical neurological and hormonal functions. In Bangladesh, the tumor is often misdiagnosed as epilepsy, hormonal disorders, or developmental delay due to limited awareness and late access to pediatric neurosurgical services. 🧬 Causes and Characteristics Craniopharyngiomas are believed to arise from embryonic remnants of the Rathke’s pouch, a structure involved in pituitary gland development. They may contain solid, cystic, or calcified components and can grow slowly over time. Two Main Types: Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma (most common in children): Often cystic and calcified Papillary Craniopharyngioma (rare in children): More solid, usually in adults These tumors can grow large enough to affect surrounding brain structures and must be evaluated by a specialist pediatric neurosurgeon. 🔍 Symptoms of Pediatric Craniopharyngioma Due to its deep brain location, symptoms develop slowly and are often subtle: Progressive vision problems (blurry vision, double vision, loss of peripheral vision) Hormonal disturbances (growth failure, delayed puberty, excessive urination and thirst) Headaches and nausea (from increased intracranial pressure) Behavioral changes, mood swings, and poor school performance Obesity or extreme weight gain Seizures (less common but possible) Short stature or developmental delay in young children In Bangladesh, many children are brought in months after symptom onset, increasing the risk of permanent hormonal and visual impairment. 🧪 Diagnostic Workup Early diagnosis requires a high index of suspicion and appropriate imaging. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman follows a comprehensive evaluation process: MRI of Brain (with contrast) – Identifies tumor size, cysts, calcifications, and relation to optic nerves and hypothalamus CT Scan – Useful for detecting calcifications Hormonal profile – To assess pituitary function (GH, ACTH, TSH, LH/FSH, prolactin, cortisol) Ophthalmological evaluation – Visual acuity and field testing Neuropsychological testing – For behavioral and learning impact (if needed) In Dhaka, these investigations are readily available at NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre, where Dr. Nafaur leads a multidisciplinary team. 🛠️ Surgical Management of Craniopharyngioma Surgery is the cornerstone of treatment, with the goal of maximal safe tumor removal while preserving vision and hormonal function. Surgical Approaches: Transcranial Surgery (Open Craniotomy) – For large or calcified tumors Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery – Minimally invasive, suitable for selected tumors close to the sellar region Cyst drainage or Ommaya reservoir placement – For large fluid-filled cysts Shunt surgery – If hydrocephalus (fluid build-up) is present “Pediatric Craniopharyngioma surgery requires precision and experience. Our goal is not just tumor removal, but also preserving quality of life, vision, and hormonal balance.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Dr. Nafaur has successfully managed multiple pediatric craniopharyngioma cases in Bangladesh, even in complex or recurrent scenarios. 🌈 Long-Term Management & Follow-Up Because craniopharyngiomas are located near critical structures, recurrence is possible even after surgery. A child with this condition needs lifelong follow-up, which includes: Hormone replacement therapy (growth hormone, thyroid, adrenal hormones, etc.) Regular MRI scans to monitor for recurrence Visual monitoring Neuropsychological support for learning or behavior issues Weight and metabolic management, especially if hypothalamic damage occurs Dr. Nafaur ensures holistic long-term care in coordination with pediatric endocrinologists, ophthalmologists, and rehabilitation specialists. 🏥 Pediatric Craniopharyngioma in Bangladesh – Current Challenges Despite being treatable, craniopharyngiomas pose a significant challenge in the Bangladeshi context due to: Low awareness among parents and primary care doctors Misdiagnosis as epilepsy or psychiatric illness Delayed referral to pediatric neurosurgery centers Inadequate imaging or hormonal evaluation in rural areas Limited availability of pediatric endocrinology services As one of the leading pediatric brain tumor specialists in Bangladesh, Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman is focused on addressing these gaps through outreach, early diagnosis, and affordable surgical treatment. 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Experienced pediatric neurosurgeon trained in advanced craniopharyngioma surgery 🇧🇩 Serving at NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 💉 Uses modern techniques like neuronavigation, endoscopic surgery, and intraoperative monitoring 🧬 Works with top pediatric endocrinologists and ophthalmologists in Bangladesh 💯 Excellent patient outcomes with compassionate, lifelong follow-up care 📞 Contact for Craniopharyngioma Surgery in Children Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com