Subdural and Subarachnoid Hemorrhages
Subdural and Subarachnoid Hemorrhages
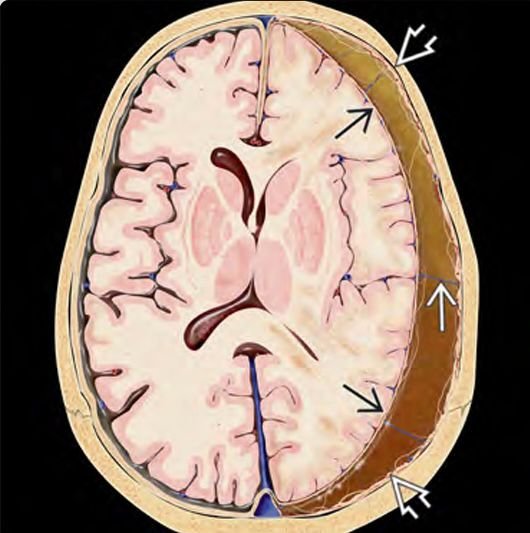
Pediatric subdural and subarachnoid hemorrhages are two of the most critical forms of intracranial bleeding in children, especially following trauma, birth injury, abuse (non-accidental trauma), or vascular malformations. These conditions can lead to rapid neurological deterioration, seizures, coma, and even death if not identified and managed promptly. In Bangladesh, delayed access to specialized pediatric neurosurgical care, lack of awareness, and limited imaging facilities often worsen the prognosis. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, a leading pediatric neurosurgeon, offers comprehensive diagnosis, emergency surgery, and neurocritical care for infants and children with subdural and subarachnoid hemorrhages. What is a Subdural Hemorrhage (SDH)? A subdural hemorrhage occurs when blood collects between the dura mater (the brain’s outer covering) and the arachnoid membrane, usually due to tearing of bridging veins following: Blunt head trauma Non-accidental trauma (Shaken Baby Syndrome) Fall from height or accident Birth trauma (in neonates) Coagulopathies (bleeding disorders) Subdural hemorrhages are more common in infants and toddlers due to their developing skull and vulnerable venous system. What is a Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)? A subarachnoid hemorrhage involves bleeding into the subarachnoid space, the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater. It can be caused by: Rupture of cerebral aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) Severe trauma Coagulopathies or infections SAH in children is often a surgical emergency and requires immediate neurosurgical evaluation to prevent fatal outcomes. Common Symptoms in Pediatric Patients Children and infants with subdural or subarachnoid hemorrhage may show: Sudden unconsciousness or coma Seizures Bulging fontanelle in infants Persistent vomiting Irritability or lethargy Unequal pupils or abnormal eye movements Difficulty breathing Neck stiffness (in SAH) Developmental regression in chronic cases Diagnosis in Bangladesh: Role of Early Imaging Prompt imaging is key to saving a child's life. Dr. Nafaur Rahman uses the following diagnostic tools: Neuroimaging CT Scan of the brain – to detect fresh bleeds, midline shift, or raised intracranial pressure MRI brain and spine – for chronic subdural collections, vascular malformations, or associated spine involvement CT Angiography/MR Angiography – to detect aneurysms or AVMs causing subarachnoid hemorrhage Other Tests Fundoscopy – may show retinal hemorrhages in abusive cases Coagulation profile – especially in neonates or children with bleeding disorders Lumbar puncture – contraindicated in raised ICP but may help confirm SAH Treatment Options by Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Dr. Nafaur Rahman provides individualized treatment depending on the size, location, and cause of the hemorrhage. For Subdural Hemorrhage: Burr hole evacuation for acute SDH in neonates and infants Craniotomy in cases with thick clots, large hematoma, or brain herniation Drain placement for slow re-accumulating hematomas Subduro-peritoneal shunt in chronic cases with fluid build-up For Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Microsurgical clipping or endovascular coiling (in collaboration with neurovascular team) External Ventricular Drain (EVD) to relieve pressure and monitor CSF Decompressive craniectomy in case of massive brain swelling Medical management of vasospasm, seizures, and raised ICP Postoperative Care & Rehabilitation Neurocritical care unit monitoring (at NINS or affiliated center) Anti-seizure medications and ICP management Neuro-rehabilitation including physiotherapy, speech therapy, and cognitive support Long-term follow-up to monitor development and learning ability Prognosis and Long-Term Effects Without timely treatment, pediatric subdural and subarachnoid hemorrhages can cause: Permanent neurological deficits Visual or hearing loss Hydrocephalus requiring VP shunt Cerebral palsy or developmental delay Death in severe untreated cases Early diagnosis and surgical intervention significantly improve survival and quality of life. Challenges in Bangladesh Delayed referrals from primary healthcare providers Limited pediatric neurosurgery expertise outside Dhaka Underreporting of child abuse-related injuries Lack of neuroimaging in district-level hospitals Poor parental awareness of early warning signs Dr. Nafaur Rahman emphasizes the need for national awareness programs and better referral systems to tackle these challenges. Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? One of Bangladesh’s most experienced pediatric neurosurgeons Specialized in neonatal and infant brain surgery Expert in trauma-related and vascular pediatric neurosurgery Offers round-the-clock emergency care and long-term follow-up Known for family-centered, compassionate neurosurgical care For Emergency or Appointment: Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Contact for Serial / Emergency Consultation: 📱 +8801912988182 | +8801607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com
YouTube Videos and Patient Reviews on Subdural and Subarachnoid Hemorrhages