Esthesioneuroblastomas
Esthesioneuroblastomas
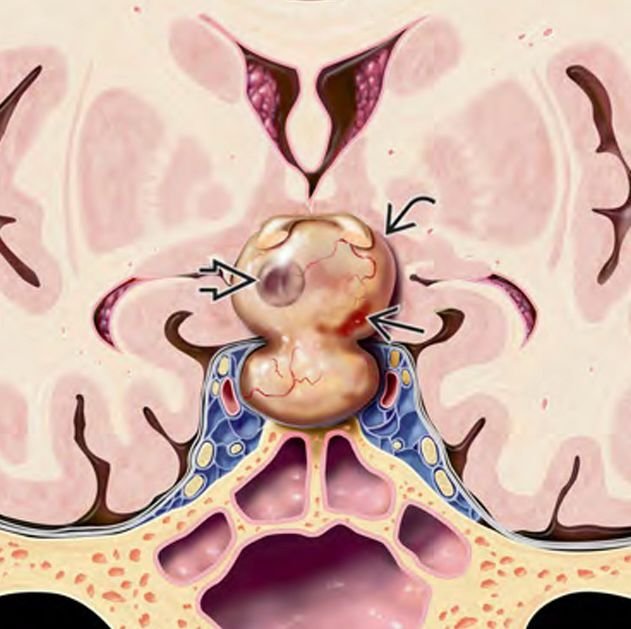
Esthesioneuroblastoma, also known as olfactory neuroblastoma, is a rare malignant tumor arising from the olfactory neuroepithelium located in the upper nasal cavity near the skull base. Although primarily diagnosed in adults, esthesioneuroblastoma can also affect pediatric patients, posing significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to its proximity to critical brain structures and vital neurovascular pathways. In Bangladesh, early diagnosis and multidisciplinary management of pediatric esthesioneuroblastomas are essential to improve survival and preserve neurological function. Under the expert care of Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, children receive advanced surgical treatment combined with radiotherapy and chemotherapy when necessary, ensuring comprehensive care tailored to pediatric needs. Epidemiology and Importance in Bangladesh Esthesioneuroblastomas are extremely rare in children, accounting for less than 5% of all pediatric nasal cavity tumors. Due to limited awareness and diagnostic capabilities in many regions of Bangladesh, diagnosis is often delayed, leading to advanced-stage presentations. Specialized centers such as the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and the Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre play a critical role in early detection and management. Causes and Pathophysiology Originates from the olfactory neuroepithelium in the superior nasal vault Malignant tumor with potential for local invasion into the skull base, orbit, and anterior cranial fossa May metastasize to cervical lymph nodes and distant sites if untreated Etiology remains unclear but may involve genetic and environmental factors Clinical Presentation Symptoms in pediatric patients are often nonspecific and may include: Nasal obstruction and congestion Recurrent nosebleeds (epistaxis) Loss or reduction of sense of smell (anosmia) Facial swelling or deformity in advanced cases Headaches or neurological signs if tumor invades skull base or brain Visual disturbances if orbital involvement occurs Lymphadenopathy if regional metastasis present Early symptoms can be mistaken for common pediatric upper respiratory infections, causing delays in diagnosis. Diagnostic Approach Imaging Studies MRI with contrast is the preferred modality to assess tumor extent, intracranial invasion, and relation to neurovascular structures CT scan helps evaluate bony destruction of the skull base and paranasal sinuses PET-CT may be used for staging and detecting metastases Histopathological Confirmation Biopsy via endoscopic nasal approach or open surgery Immunohistochemistry to differentiate from other small round blue cell tumors Other Evaluations Comprehensive ENT and neurological examination Assessment for cervical lymphadenopathy with ultrasound or CT neck Ophthalmologic evaluation if orbit involved Treatment Modalities Surgical Resection Primary treatment involves complete surgical excision of the tumor with clear margins Approaches include endoscopic endonasal surgery or craniofacial resection, depending on tumor extent Preservation of neurological function and cosmesis are priorities in pediatric patients Dr. Nafaur Rahman utilizes cutting-edge microsurgical and endoscopic techniques for maximal safe resection Radiotherapy Adjuvant radiotherapy is often recommended postoperatively to reduce recurrence risk Careful planning to minimize radiation exposure to developing brain tissue in children Chemotherapy Used in advanced or metastatic disease and sometimes as neoadjuvant therapy to shrink tumors before surgery Pediatric oncology collaboration is essential Prognosis and Follow-up Prognosis depends on tumor stage, extent of resection, and response to adjuvant therapies Early-stage tumors have favorable outcomes with long-term survival Close follow-up with serial imaging and clinical exams is vital for early detection of recurrence Multidisciplinary rehabilitation supports neurological and functional recovery Challenges in Bangladesh Lack of awareness leading to delayed presentation in advanced stages Limited availability of specialized skull base and pediatric oncology services in rural areas Financial and logistic difficulties in accessing multimodal treatment Importance of centralized care at institutions like NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre for best outcomes Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Expertise in managing rare pediatric skull base malignancies including esthesioneuroblastomas Access to advanced surgical technology including neuronavigation and endoscopic equipment Multidisciplinary care involving neurosurgery, ENT, oncology, radiology, and rehabilitation Commitment to affordable, family-centered care for children across Bangladesh Extensive experience in pediatric neuro-oncology and skull base surgery ensuring optimal outcomes Contact Information Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Serial & Appointment: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com