Multiple Suture Synostosis
Multiple Suture Synostosis
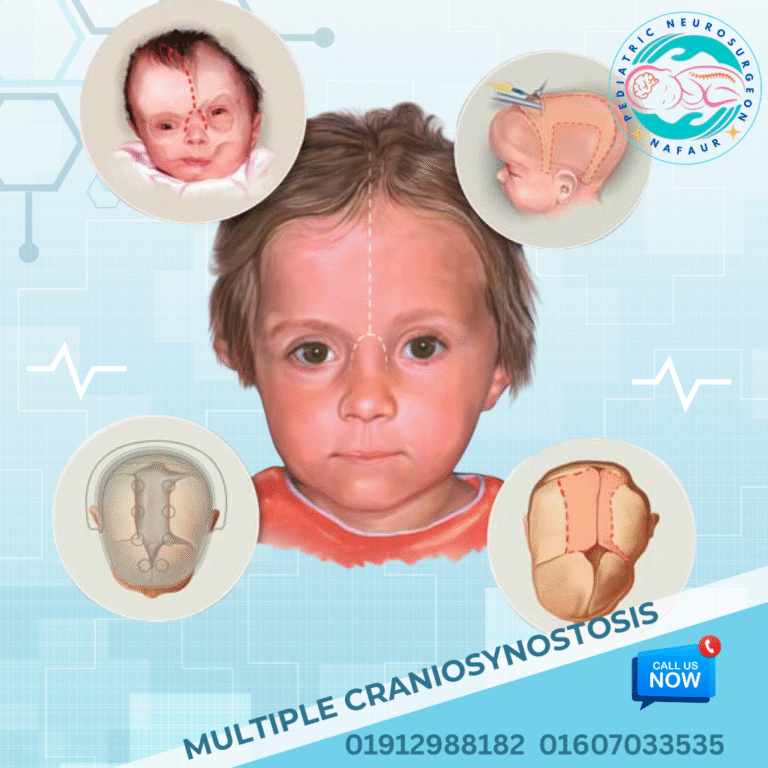
Multiple suture synostosis refers to the premature fusion of two or more cranial sutures in an infant’s skull. This condition is a more complex and severe form of craniosynostosis, leading to significant abnormalities in skull shape and potential neurodevelopmental complications. The normal sutures—fibrous joints between skull bones—allow the skull and brain to grow during infancy. When multiple sutures close too early, it restricts skull growth in multiple dimensions, potentially increasing intracranial pressure and causing abnormal head shapes. 🌍 Multiple Suture Synostosis in the Bangladesh Context In Bangladesh, awareness about multiple suture synostosis is limited, especially outside urban centers like Dhaka Early diagnosis is often delayed due to lack of newborn screening programs and limited pediatric neurosurgical expertise in rural areas Many children present with complex skull deformities and neurodevelopmental delays by the time of first consultation Advanced pediatric neurosurgical care and multidisciplinary treatment at National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre improve outcomes Public health initiatives are needed to increase awareness and timely referral for affected children ⚠️ Causes and Risk Factors Genetic syndromes such as Crouzon syndrome, Apert syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, and other craniosynostosis syndromes are common causes Sporadic premature fusion due to unknown causes also occurs Environmental factors including maternal nutritional deficiencies and prenatal exposures Complex craniosynostosis often involves mutations affecting cranial suture development and bone growth 🧒 Signs and Symptoms Severely abnormal skull shape depending on sutures involved (e.g., cloverleaf skull, brachycephaly, oxycephaly) Increased head circumference or restricted skull growth with compensatory deformities Possible symptoms of raised intracranial pressure: irritability, vomiting, headache, developmental delays Facial abnormalities such as midface hypoplasia, proptosis (bulging eyes), and airway problems in syndromic cases Neurological deficits including cognitive impairment and seizures in severe or untreated cases 🔍 Diagnosis and Imaging Thorough clinical evaluation by a pediatric neurosurgeon experienced in complex craniosynostosis 3D CT scan is the imaging modality of choice for detailed visualization of fused sutures and skull deformities MRI brain to assess brain development and exclude associated anomalies Genetic testing for syndromic diagnosis Multidisciplinary assessments including pediatrics, ophthalmology, and ENT as needed 🛠️ Surgical Treatment Approaches Surgical intervention is complex and requires a multistage, multidisciplinary approach, ideally performed early in life (between 3-12 months of age) for best outcomes. Surgical Goals: Release fused sutures to allow normal brain and skull growth Reshape the skull and facial bones to improve appearance and function Relieve or prevent increased intracranial pressure Address airway and ophthalmologic complications in syndromic cases Minimize surgical risks with advanced perioperative care Common Surgical Procedures: Cranial Vault Remodeling: reshaping the skull bones extensively to correct deformities Fronto-orbital Advancement for midface and orbital correction Distraction Osteogenesis in some cases for gradual bone lengthening Multiple staged surgeries depending on severity and syndrome involvement 🏥 Postoperative Care and Follow-Up Prolonged hospital stay may be required for complex cases Intensive care monitoring for neurological and respiratory status Regular follow-up with neuroimaging to assess skull shape and brain health Long-term developmental and cognitive assessments Coordinated multidisciplinary care with pediatricians, speech therapists, ophthalmologists, and ENT specialists 🔄 Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook Early and appropriate surgical intervention improves both cosmetic and neurological outcomes Lifelong follow-up necessary for syndromic and complex cases due to risk of recurrent suture fusion and developmental challenges Multidisciplinary support optimizes quality of life and functional independence Family education and psychosocial support integral to management 👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? Highly skilled pediatric neurosurgeon with expertise in complex and syndromic craniosynostosis Leading specialist at the National Institute of Neurosciences & Hospital (NINS), Dhaka Chief Consultant at Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre, offering state-of-the-art pediatric neurosurgical care Experience with latest surgical techniques and multidisciplinary management tailored to Bangladesh’s healthcare needs Compassionate and family-focused care from diagnosis through long-term follow-up 📞 Schedule Your Child’s Consultation for Multiple Suture Synostosis Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 Call: 01912988182 | 01607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com