Atlantoaxial (C1-2) subluxation/dislocation
Atlantoaxial (C1-2) subluxation/dislocation
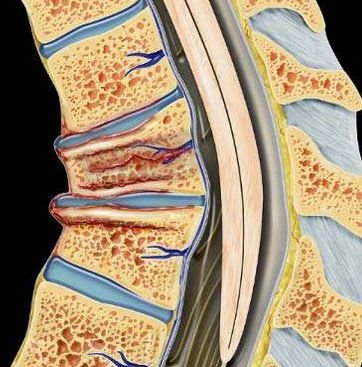
Atlantoaxial subluxation or dislocation is a serious instability or misalignment of the upper two cervical vertebrae—atlas (C1) and axis (C2). This condition can result in abnormal movement, neurological compression, and even life-threatening spinal cord injury. The C1-C2 complex is responsible for nearly 50% of neck rotation, and any trauma or instability in this region poses a major risk to spinal cord function. In the Bangladesh context, Atlantoaxial instability often arises from road traffic accidents, falls, congenital anomalies, rheumatoid arthritis, and tuberculous infections—all of which are prevalent in both urban and rural settings. Relevance in Bangladesh Despite its severity, Atlantoaxial subluxation/dislocation is frequently underdiagnosed in Bangladesh due to limited early access to advanced spinal imaging and neurosurgical expertise. Patients often present late with neurological symptoms, such as limb weakness, difficulty walking, or even paralysis. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, a leading pediatric and spinal neurosurgeon in Bangladesh, is highly experienced in managing both congenital and traumatic C1-C2 instabilities through modern surgical interventions, ensuring safe outcomes even in complex cases. Causes of Atlantoaxial Subluxation/Dislocation 🔹 Traumatic Road traffic accidents Falls from height or staircases Diving or sports-related injuries 🔹 Non-Traumatic Congenital anomalies (e.g., Os odontoideum, Down Syndrome) Rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile idiopathic arthritis Tuberculosis (common in Bangladesh – Grisel’s syndrome) Inflammatory or infectious causes (retropharyngeal abscess) Symptoms of Atlantoaxial Instability Neck pain and restricted neck motion Neurological symptoms like weakness, numbness, or tingling in arms/legs Unsteady gait or frequent falling (ataxia) Torticollis (abnormal neck posture) Bladder/bowel dysfunction In severe cases, respiratory difficulty or sudden paralysis Children may present with subtle signs, making early detection critical. Diagnostic Imaging & Evaluation Dr. Nafaur Rahman emphasizes prompt imaging and clinical evaluation, especially in high-risk or symptomatic patients: X-ray (open mouth view, lateral dynamic view) – Identifies instability CT scan (3D reconstruction) – Shows bone alignment and fractures MRI of cervical spine – Evaluates spinal cord compression and ligament integrity Neurological exam – Assesses motor and sensory deficits Diagnosis is confirmed by detecting abnormal atlantodental interval (ADI) or malalignment of C1-C2 vertebrae. Classification of Atlantoaxial Instability Rotatory Subluxation – Common in children, may follow minor trauma or infection Posterior/Anterior Dislocation – Often traumatic, may compress spinal cord Vertical Subluxation (Basilar Invagination) – Associated with congenital or rheumatoid disorders Each type requires a customized treatment plan based on stability and neurological status. Treatment Approaches in Bangladesh Treatment of Atlantoaxial dislocation requires specialized surgical expertise, and Dr. Nafaur Rahman follows global protocols adapted to the local healthcare environment. ✅ Non-Surgical Management (For Mild, Reducible Cases) Cervical immobilization with collar or halo vest Anti-inflammatory therapy if associated with infection Antibiotics and anti-TB drugs for tuberculous origin Close monitoring with serial imaging This approach is suitable for pediatric patients with rotatory subluxation or Grisel’s syndrome if no cord compression is present. ✅ Surgical Intervention (For Irreducible or Neurologically Compromising Cases) Surgical stabilization is the mainstay in cases of: Irreducible dislocation Spinal cord compression Progressive neurological deficits Congenital anomalies or os odontoideum Common Surgical Procedures Include: C1-C2 posterior fixation (Goel-Harms technique) Transarticular screw fixation Occipito-cervical fusion for craniovertebral instability Anterior decompression (in selected cases) Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman utilizes intraoperative neuromonitoring and advanced spinal instrumentation systems to ensure safe correction with minimal risk. Postoperative Care and Prognosis Hospital stay: Typically 4–6 days Collar immobilization: 6–12 weeks Physiotherapy: Gradual restoration of neck mobility Regular follow-up X-rays to ensure spinal fusion and stability Most patients regain normal function with timely surgery Why Choose Dr. Nafaur Rahman for C1-C2 Spine Surgery? ✔️ Specialized in craniovertebral junction surgeries ✔️ More than a decade of experience in complex pediatric spinal cases ✔️ Access to modern ORs, navigation, and neuromonitoring ✔️ High success rates with low complication profiles ✔️ Based at the National Institute of Neurosciences (NINS) and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre Book an Urgent Evaluation for Neck Trauma or Instability 📌 Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📞 For Serial/Appointment: 📱 +8801912988182 | +8801607033535 🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com