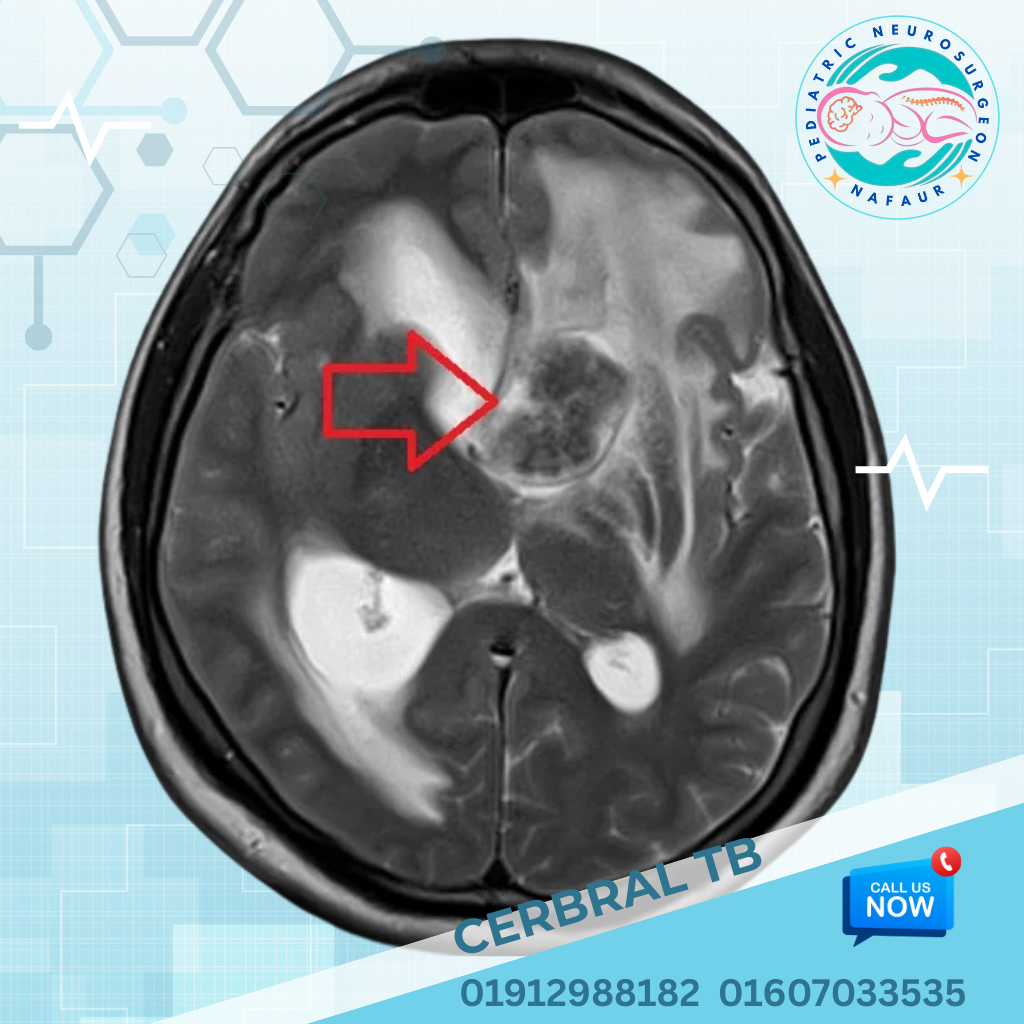
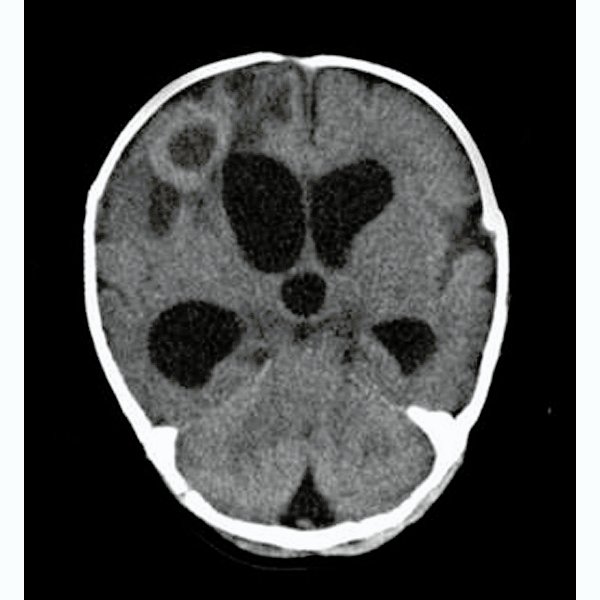
Cerebral TB
Cerebral TB
Pediatric cerebral tuberculosis is a dangerous neurological form of tuberculosis (TB) that affects the central nervous system (CNS) of children. It may present as: TB Meningitis (infection of the brain’s covering) Tuberculoma (localized brain mass caused by TB bacteria) TB Abscess or hydrocephalus due to TB blockage of CSF flow Spinal arachnoiditis or vertebral TB in some cases Cerebral TB in children is a medical emergency that requires urgent attention. If not diagnosed and treated early, it can result in permanent brain damage, developmental delay, blindness, paralysis, or even death. 🌍 Pediatric TB of the Brain – A Growing Threat in Bangladesh Bangladesh remains a high TB burden country. Despite national TB programs, neurotuberculosis in children is underdiagnosed and often referred late due to vague symptoms, low awareness, and limited neuroimaging in rural settings. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman, with advanced neurosurgical training and vast experience in neuroinfectious diseases, leads the fight against pediatric cerebral TB, combining diagnostic precision, life-saving surgeries, and multidisciplinary rehabilitation. Key Factors Contributing to Pediatric Cerebral TB in Bangladesh: 🧬 Malnutrition and poor immunity in children 🏘️ Overcrowding and poor ventilation in rural homes ❌ Incomplete treatment of systemic TB or contact with TB-positive adults ⏳ Delay in recognizing neurological signs and symptoms 💉 Lack of access to MRI and pediatric neurosurgery in remote districts ⚠️ Signs and Symptoms of Pediatric Cerebral TB The symptoms are slowly progressive, which often delays diagnosis. Common warning signs include: 🌡️ Persistent fever (more than 2 weeks) 🧠 Headache, vomiting, and drowsiness 🧒 Delayed milestones or regression in toddlers 👁️ Vision problems or squint (cranial nerve palsies) ⚡ Seizures, especially focal or prolonged ones 🚶 Limb weakness or abnormal walking 🛌 Altered consciousness or coma in advanced stages “Any child in Bangladesh with prolonged fever, neurological symptoms, and failure to thrive must be evaluated for TB meningitis or tuberculoma.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🧬 Causes and Types of Pediatric Cerebral TB Cerebral TB results when Mycobacterium tuberculosis spreads to the brain through blood or CSF from a lung infection or lymph node TB. Common Neurological TB Conditions in Children: TB Meningitis – Most common, causes inflammation of brain lining and hydrocephalus Tuberculoma – Solid granulomatous lesion in brain parenchyma, mimics brain tumor TB Abscess – Rare, forms pus-filled cavity in brain TB Arachnoiditis – Inflammation around spinal cord Vertebral TB (Pott’s disease) – Involves spine, often seen with neurological TB 🧪 Diagnosis of Pediatric Cerebral TB in Bangladesh Dr. Nafaur Rahman ensures accurate diagnosis using modern neuroimaging and laboratory support available at NINS and Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre. Essential Investigations: 🧠 MRI Brain with Contrast – Best for detecting tuberculoma, meningitis, abscess 📸 CT Scan – Useful in emergencies or hydrocephalus cases 🧫 CSF Analysis – Shows elevated protein, low glucose, lymphocytic pleocytosis 🔬 CBNAAT / GeneXpert TB-PCR from CSF – Confirms TB bacteria 🧍♂️ Chest X-ray – To detect pulmonary TB source 🧪 Blood tests – ESR, Mantoux test, TB IgM/IgG 🛠️ Treatment of Pediatric Cerebral TB Treatment involves a combination of anti-tubercular therapy (ATT) and neurosurgical interventions when required. 💊 Medical Therapy: ATT for 12–18 months, including Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Pyrazinamide, Ethambutol Steroids (Dexamethasone) to reduce brain inflammation Seizure control medications Nutritional support 🧠 Surgical Intervention: Dr. Nafaur Rahman performs surgery in cases of: Obstructive hydrocephalus Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt to divert CSF and reduce pressure Large Tuberculoma or TB Abscess Microsurgical excision if mass is causing pressure or seizures Image-guided, safe, and often life-saving Brain Biopsy If diagnosis is unclear or resistant to ATT Helps in confirming drug-resistant TB strains “Not all cases of brain TB need surgery, but when they do—timely and precise intervention can mean the difference between recovery and permanent damage.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman 🔁 Long-Term Care and Rehabilitation Recovery from cerebral TB is possible with comprehensive follow-up and rehabilitation: 🧠 Repeat MRI/CT every 3–6 months ⚕️ Neurodevelopmental assessments 🧒 Speech, physiotherapy, and cognitive therapy 🧑⚕️ Regular monitoring for hearing, vision, and behavior 📚 Educational support for school-age children 🚫 Prevention of recurrence through BCG vaccination and family screening 🚨 Complications of Delayed or Inadequate Treatment 🧠 Brain herniation or coma ⚡ Intractable seizures 🧑🦽 Motor deficits or spasticity 👁️ Permanent blindness or cranial nerve palsy 🛌 Developmental regression and learning difficulties ⚰️ Death due to brainstem involvement or hydrocephalus Early diagnosis, complete ATT, and surgical referral when necessary save lives. 👨⚕️ Why Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman? 🧠 Leading pediatric neurosurgeon in Bangladesh for TB-related brain complications 🏥 Operates at NINS, the country’s premier neurology and neurosurgery hospital 🧒 Expert in minimally invasive surgery for TB hydrocephalus and tuberculoma 🌐 Dedicated to early referral systems and rural awareness programs 🤝 Collaborates with pediatricians and public health teams for holistic care 📞 Contact Dr. Nafaur Rahman for Expert Care in Pediatric Brain TB Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre 📱 For Serial/Appointment: 📞 01912988182 | 📞 01607033535 🌐 Website: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com