Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
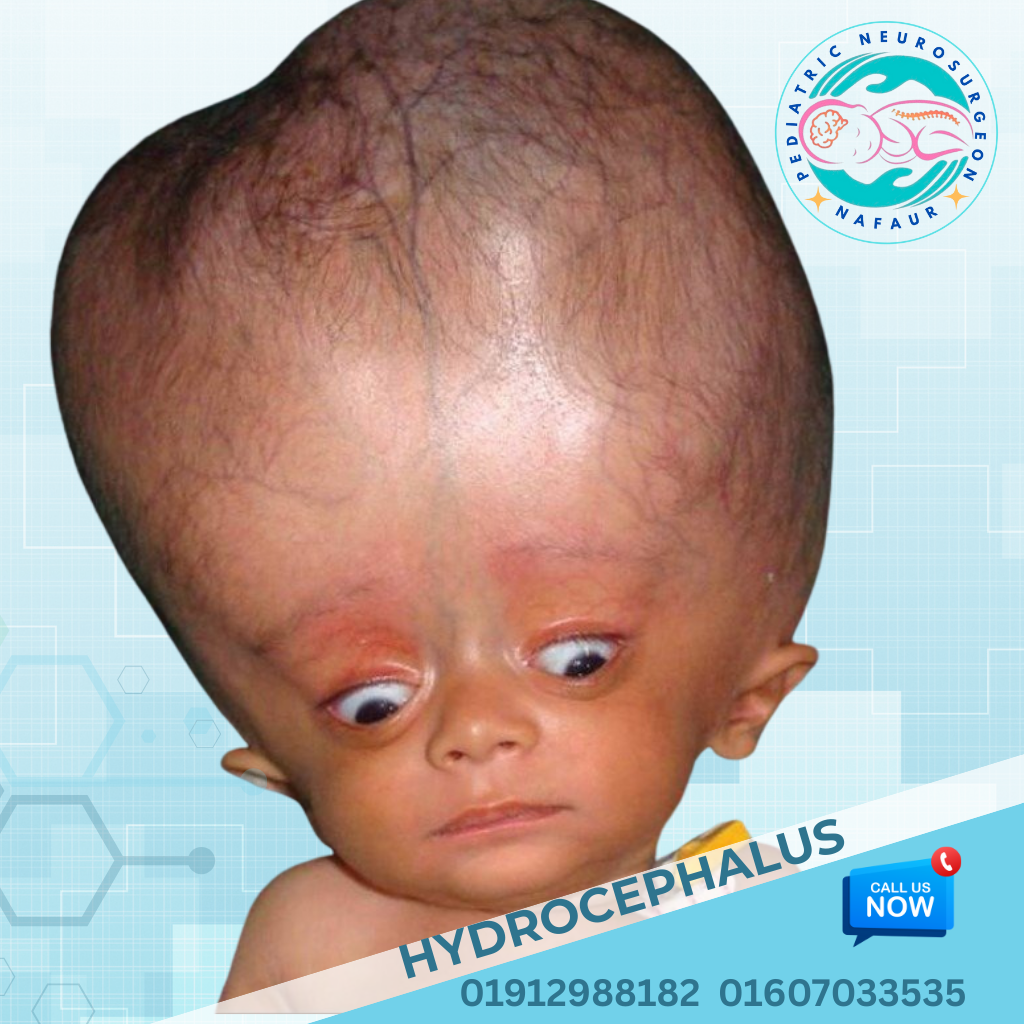
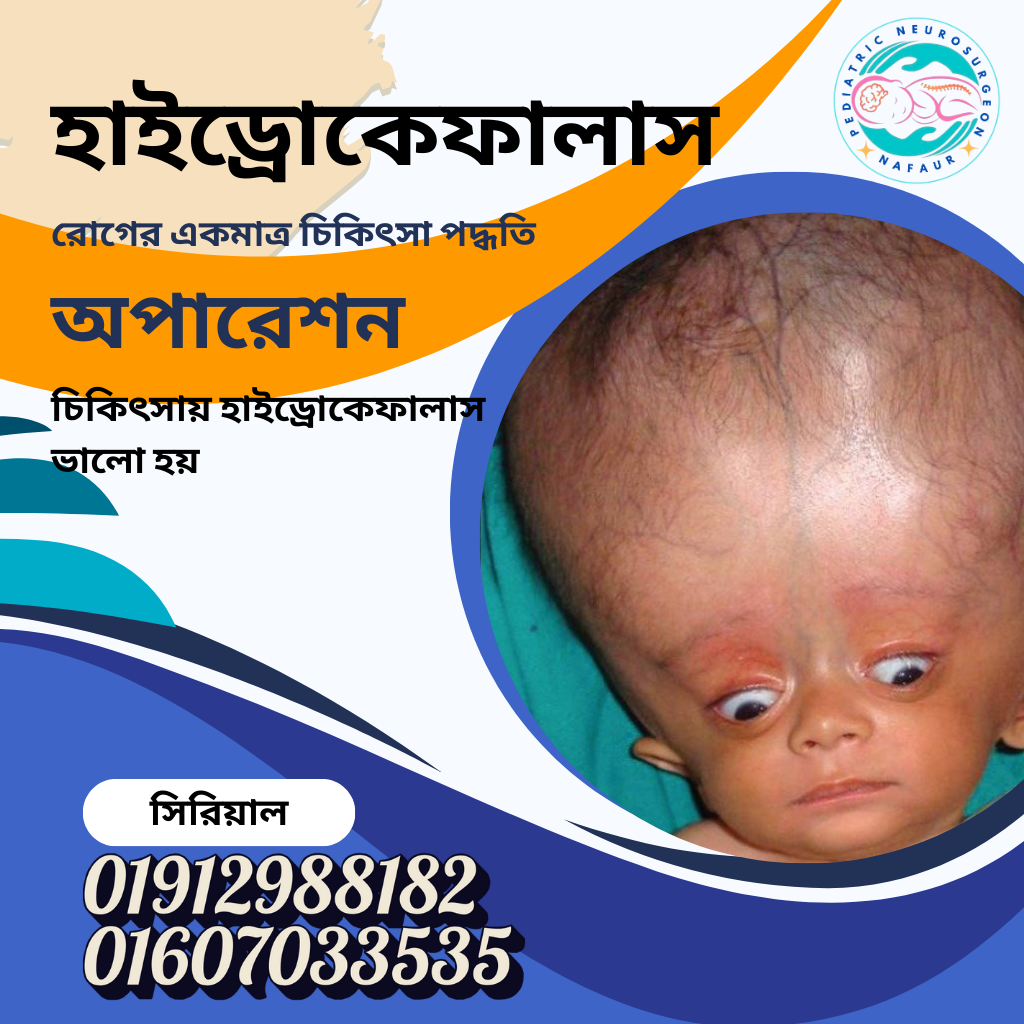
Pediatric hydrocephalus is a neurological condition in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates in the brain's ventricles, leading to increased pressure inside the skull. It is often referred to as "water on the brain" and can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (after birth due to infections, hemorrhage, tumors, or trauma).
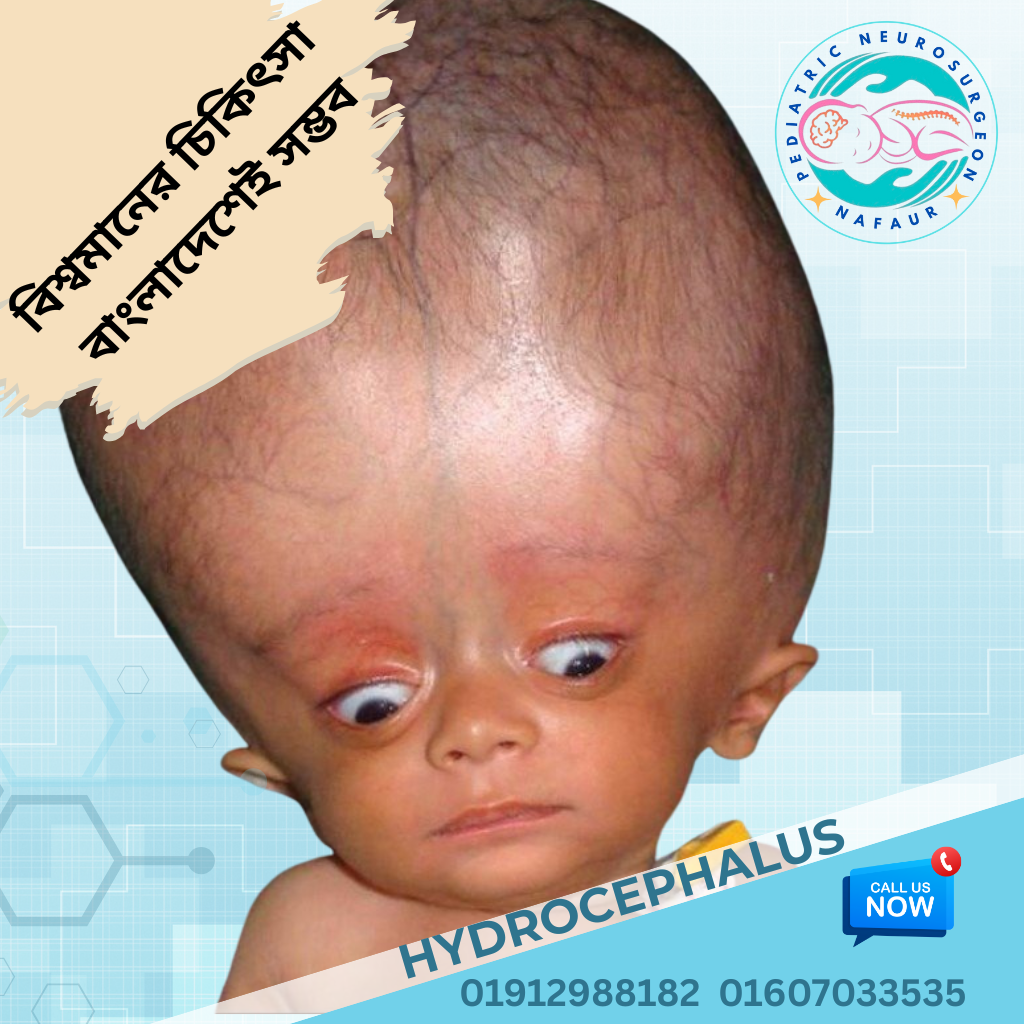
In Bangladesh, hydrocephalus remains one of the most common causes of brain damage and disability in children, especially in underserved areas. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent brain damage, blindness, delayed development, seizures, and even death. However, with timely diagnosis and appropriate surgical treatment, most children can lead healthy, productive lives.
👶 Common Causes of Hydrocephalus in Children
1. Congenital Hydrocephalus
Aqueductal stenosis (narrowing of brain canal)
Neural tube defects (e.g., spina bifida)
Genetic syndromes
Dandy-Walker malformation
2. Post-Infectious Hydrocephalus
Neonatal meningitis
Tubercular meningitis (TBM) — common in rural Bangladesh
Brain abscess complications
3. Post-Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus
Premature birth with intraventricular hemorrhage
Birth trauma
4. Hydrocephalus Secondary to Tumors
Tumors obstructing CSF pathways (e.g., medulloblastoma, craniopharyngioma)
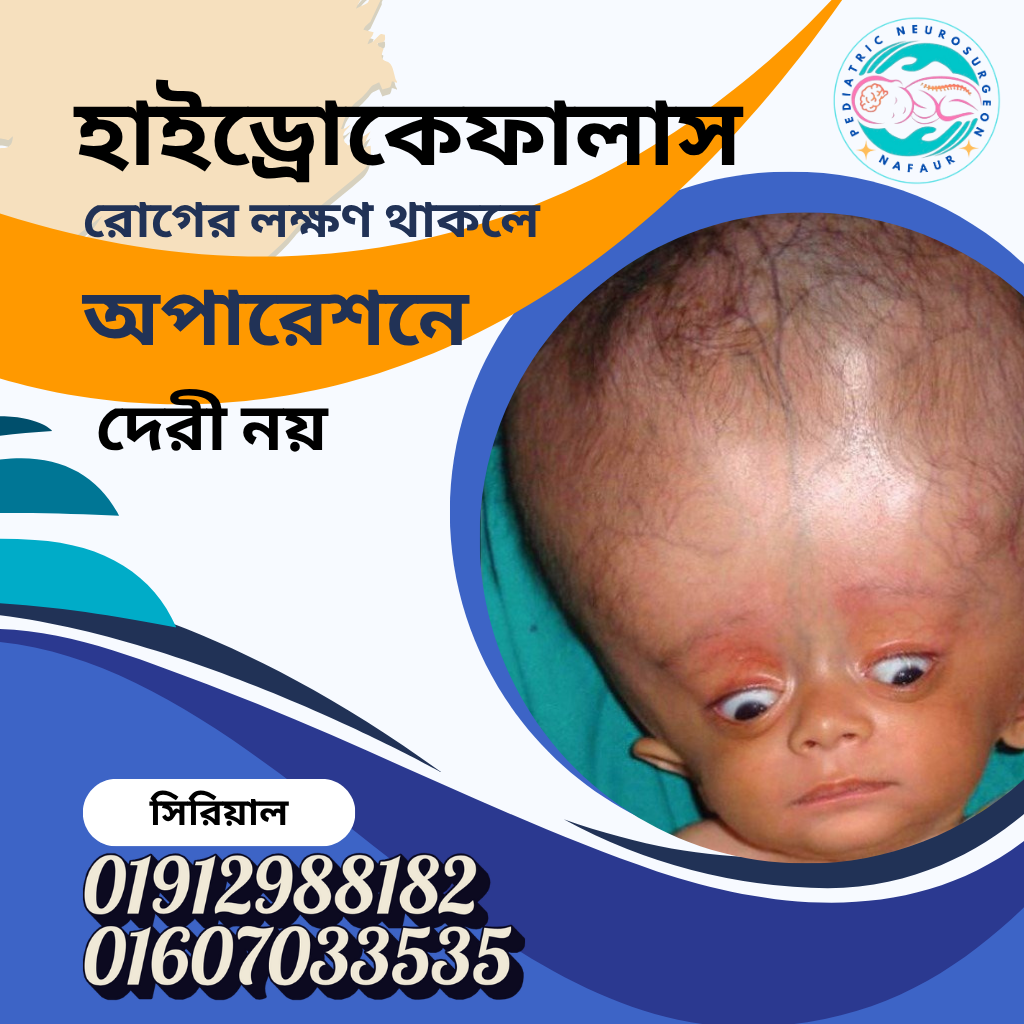
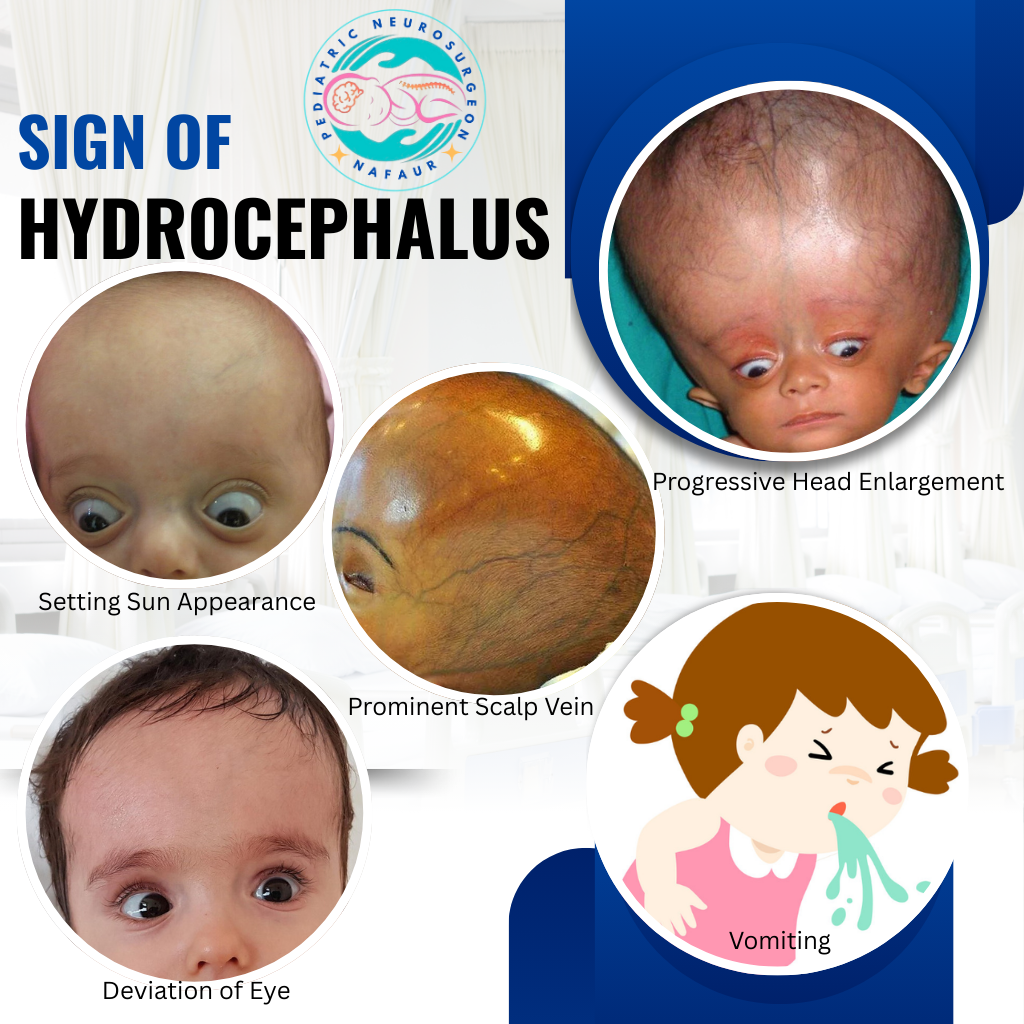
🧠 Signs and Symptoms – What to Watch for in Children
Recognizing hydrocephalus early can save a child’s brain. Common signs include:
Rapid or abnormal head growth
Bulging soft spot (anterior fontanelle)
Vomiting, irritability, poor feeding
Downward gaze (“sun-setting” eyes)
Seizures
Delayed milestones or loss of consciousness in older children
In Bangladesh, many families miss these early signs due to lack of awareness. Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman strongly advocates for early screening in high-risk newborns and infants.
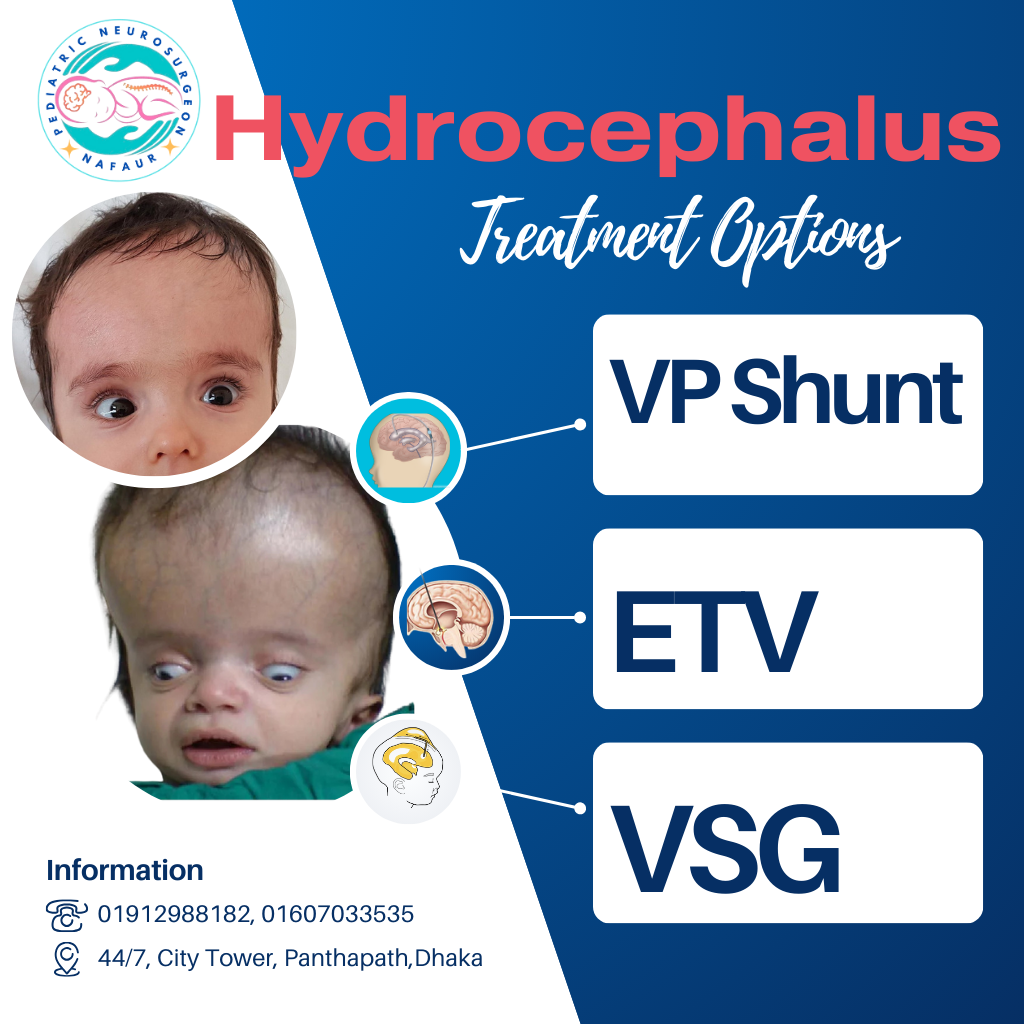
🏥 Surgical Management of Hydrocephalus
✅ 1. Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) Shunt Surgery
Most common surgery in Bangladesh for hydrocephalus
Involves placing a thin tube (shunt) from the brain ventricles to the abdomen to drain excess CSF
Requires lifetime follow-up, but highly effective when done early
Dr. Nafaur uses low-pressure programmable shunts to reduce complications
✅ 2. Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV)
A minimally invasive, shunt-free option
Ideal for obstructive hydrocephalus like aqueductal stenosis
Creates a new pathway for CSF inside the brain
Less long-term dependence compared to VP shunt
“ETV is a game-changer in select pediatric hydrocephalus cases. It avoids lifelong hardware.” — Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman
✅ 3. ETV with Choroid Plexus Cauterization (ETV-CPC)
Especially beneficial for infants in resource-limited settings like Bangladesh
Reduces CSF production along with diversion
Has shown success in replacing VP shunt in infants
✅ 4. VSG Shunt
Especially beneficial for infants with extremely low birth weight with lack of subcutaneous fat.
🔍 Bangladesh Perspective – Challenges and Realities
In Bangladesh, pediatric hydrocephalus poses significant challenges due to:
❌ Low awareness in rural healthcare systems
❌ Delays in referral and diagnosis
❌ Limited access to neuroimaging (CT/MRI) in remote areas
❌ Financial barriers to neurosurgery
❌ Shunt infections due to poor follow-up or sanitation
Dr. Nafaur Rahman addresses these challenges through:
🧠 Early diagnosis using clinical judgment and low-cost imaging
💉 Safe, affordable shunt surgery for underserved populations
🧑⚕️ Parental counseling on long-term shunt care
📊 Public education to reduce treatment delay
📈 Impact of Timely Surgery
Children treated in time for hydrocephalus often show:
✅ Improved brain development
✅ Reduced risk of blindness, seizures, and mental impairment
✅ Ability to attend school, socialize, and live independently
✅ Reduced burden on families and the healthcare system
Without surgery, hydrocephalus can lead to permanent disability, mental retardation, and even death.
👨⚕️ Why Choose Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman?
🧒 Specialized in pediatric hydrocephalus and brain development disorders
🏥 Faculty neurosurgeon at NINS, Bangladesh's top neurology institute
🛠️ Performs both VP shunt and ETV surgeries, based on individualized assessment
💬 Provides comprehensive counseling for parents on post-surgery care
🧾 Affordable treatment plans for low-income families through Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre
🧒 Rehabilitation and Follow-Up Care
Surgical treatment is only the beginning. Long-term success depends on:
Regular head circumference monitoring
Developmental screening (motor, speech, cognition)
Periodic imaging (CT/MRI to check shunt or ETV function)
Access to speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physiotherapy
Dr. Nafaur’s team provides a complete post-op neurorehabilitation pathway for all hydrocephalus patients.
📞 Contact for Pediatric Hydrocephalus Treatment
Dr. Md. Nafaur Rahman
Assistant Professor, Pediatric Neurosurgery, NINS
Chief Consultant, Bangladesh Paediatric Neurocare Centre
📞 Serial / Appointment: 01912988182 | 01607033535
🌐 Visit: www.neurosurgeonnafaur.com
Surgery for Hydrocephalus
(আরো জানতে নিচের লিঙ্কে ক্লিক করুন)